Molecular diversity of coronaviruses in bats
- PMID: 16647731
- PMCID: PMC7111821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.02.041
Molecular diversity of coronaviruses in bats
Abstract
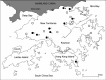
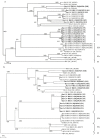
The existence of coronaviruses in bats is unknown until the recent discovery of bat-SARS-CoV in Chinese horseshoe bats and a novel group 1 coronavirus in other bat species. Among 309 bats of 13 species captured from 20 different locations in rural areas of Hong Kong over a 16-month period, coronaviruses were amplified from anal swabs of 37 (12%) bats by RT-PCR. Phylogenetic analysis of RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase (pol) and helicase genes revealed six novel coronaviruses from six different bat species, in addition to the two previously described coronaviruses. Among the six novel coronaviruses, four were group 1 coronaviruses (bat-CoV HKU2 from Chinese horseshoe bat, bat-CoV HKU6 from rickett's big-footed bat, bat-CoV HKU7 from greater bent-winged bat and bat-CoV HKU8 from lesser bent-winged bat) and two were group 2 coronaviruses (bat-CoV HKU4 from lesser bamboo bats and bat-CoV HKU5 from Japanese pipistrelles). An astonishing diversity of coronaviruses was observed in bats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic characterization of Betacoronavirus lineage C viruses in bats reveals marked sequence divergence in the spike protein of pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5 in Japanese pipistrelle: implications for the origin of the novel Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Virol. 2013 Aug;87(15):8638-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01055-13. Epub 2013 May 29. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23720729 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of bat coronavirus HKU2 from Chinese horseshoe bats revealed a much smaller spike gene with a different evolutionary lineage from the rest of the genome.Virology. 2007 Oct 25;367(2):428-39. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.06.009. Epub 2007 Jul 6. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17617433 Free PMC article.
-
Coronaviruses in bent-winged bats (Miniopterus spp.).J Gen Virol. 2006 Sep;87(Pt 9):2461-2466. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.82203-0. J Gen Virol. 2006. PMID: 16894183
-
Bat origin of human coronaviruses.Virol J. 2015 Dec 22;12:221. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0422-1. Virol J. 2015. PMID: 26689940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus diversity, phylogeny and interspecies jumping.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009 Oct;234(10):1117-27. doi: 10.3181/0903-MR-94. Epub 2009 Jun 22. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009. PMID: 19546349 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Potent, Broad-Spectrum Coronavirus Main Protease Inhibitors for Pandemic Preparedness.J Med Chem. 2024 Oct 10;67(19):17454-17471. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01404. Epub 2024 Sep 27. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39332817 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of convergent evolution of ACE2 receptor utilization among HKU5 coronaviruses.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 28:2024.08.28.608351. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.28.608351. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39253417 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Comparative Performance in the Detection of Four Coronavirus Genera from Human, Animal, and Environmental Specimens.Viruses. 2024 Mar 29;16(4):534. doi: 10.3390/v16040534. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675878 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Bias in Sample Collections From Bats, the Culprit of SARS Coronavirus, SARS-Coronavirus-2, and Other Emerging Viruses.Infect Microbes Dis. 2020 Oct 6;2(4):173-174. doi: 10.1097/IM9.0000000000000036. eCollection 2020 Dec. Infect Microbes Dis. 2020. PMID: 38630082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Unveiling hidden structural patterns in the SARS-CoV-2 genome: Computational insights and comparative analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 4;19(4):e0298164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298164. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38574063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eickmann M., Becker S., Klenk H.D., Doerr H.W., Stadler K., Censini S., Guidotti S., Masignani V., Scarselli M., Mora M., Donati C., Han J.H., Song H.C., Abrignani S., Covacci A., Rappuoli R. Phylogeny of the SARS coronavirus. Science. 2003;302:1504–1505. - PubMed
-
- Guan Y., Zheng B.J., He Y.Q., Liu X.L., Zhuang Z.X., Cheung C.L., Luo S.W., Li P.H., Zhang L.J., Guan Y.J., Butt K.M., Wong K.L., Chan K.W., Lim W., Shortridge K.F., Yuen K.Y., Peiris J.S., Poon L.L. Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science. 2003;302:276–278. - PubMed
-
- Jonassen C.M., Kofstad T., Larsen I.L., Lovland A., Handeland K., Follestad A., Lillehaug A. Molecular identification and characterization of novel coronaviruses infecting graylag geese (Anser anser), feral pigeons (Columbia livia) and mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) J. Gen. Virol. 2005;86:1597–1607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

