A pharmacological map of the PI3-K family defines a role for p110alpha in insulin signaling
- PMID: 16647110
- PMCID: PMC2946820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.035
A pharmacological map of the PI3-K family defines a role for p110alpha in insulin signaling
Abstract
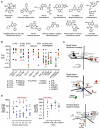
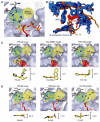
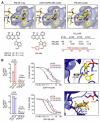
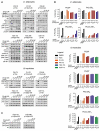
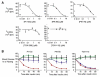
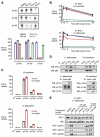
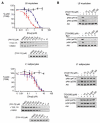
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3-Ks) are an important emerging class of drug targets, but the unique roles of PI3-K isoforms remain poorly defined. We describe here an approach to pharmacologically interrogate the PI3-K family. A chemically diverse panel of PI3-K inhibitors was synthesized, and their target selectivity was biochemically enumerated, revealing cryptic homologies across targets and chemotypes. Crystal structures of three inhibitors bound to p110gamma identify a conformationally mobile region that is uniquely exploited by selective compounds. This chemical array was then used to define the PI3-K isoforms required for insulin signaling. We find that p110alpha is the primary insulin-responsive PI3-K in cultured cells, whereas p110beta is dispensable but sets a phenotypic threshold for p110alpha activity. Compounds targeting p110alpha block the acute effects of insulin treatment in vivo, whereas a p110beta inhibitor has no effect. These results illustrate systematic target validation using a matrix of inhibitors that span a protein family.
Figures
Comment in
-
Using isoform-specific inhibitors to target lipid kinases.Cell. 2006 May 19;125(4):647-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.008. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16713558
Similar articles
-
Evidence for functional redundancy of class IA PI3K isoforms in insulin signalling.Biochem J. 2007 Jun 15;404(3):449-58. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070003. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17362206 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role for the p110alpha phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase in growth and metabolic regulation.Nature. 2006 May 18;441(7091):366-70. doi: 10.1038/nature04694. Epub 2006 Apr 12. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16625210
-
Dominant role of the p110beta isoform of PI3K over p110alpha in energy homeostasis regulation by POMC and AgRP neurons.Cell Metab. 2009 Nov;10(5):343-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.09.008. Cell Metab. 2009. PMID: 19883613 Free PMC article.
-
Should individual PI3 kinase isoforms be targeted in cancer?Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;21(2):199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.12.007. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19200708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties of FDA-approved small molecule phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors prescribed for the treatment of malignancies.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jun;168:105579. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105579. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33774181 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond PI3Ks: targeting phosphoinositide kinases in disease.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023 May;22(5):357-386. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00582-5. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 36376561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K signalling in B- and T-lymphocytes: new developments and therapeutic advances.Biochem J. 2012 Mar 15;442(3):465-81. doi: 10.1042/BJ20112092. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22364281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autocrine FGF1 signaling promotes glucose uptake in adipocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 4;119(40):e2122382119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2122382119. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36161959 Free PMC article.
-
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway in normal and malignant B cells: activation mechanisms, regulation and impact on cellular functions.Front Immunol. 2012 Aug 9;3:224. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00224. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22908014 Free PMC article.
-
Purine analogs as phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIβ inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Jun 1;26(11):2706-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27090557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alaimo PJ, Knight ZA, Shokat KM. Targeting the gate-keeper residue in phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005;13:2825–2836. - PubMed
-
- Asano T, Kanda A, Katagiri H, Nawano M, Ogihara T, Inukai K, Anai M, Fukushima Y, Yazaki Y, Kikuchi M, et al. p110beta is up-regulated during differentiation of 3T3–L1 cells and contributes to the highly insulin-responsive glucose transport activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:17671–17676. - PubMed
-
- Barvian NC, Kolz CN, Para KS, Patt WC, Viskick M. Benzoxazin-3-ones and derivatives thereof as inhibitors of PI3K. WO 04/052373 Jun, 2004.
-
- Bi L, Okabe I, Bernard DJ, Wynshaw-Boris A, Nussbaum RL. Proliferative defect and embryonic lethality in mice homozygous for a deletion in the p110alpha subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:10963–10968. - PubMed
-
- Bi L, Okabe I, Bernard DJ, Nussbaum RL. Early embryonic lethality in mice deficient in the p110beta catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase. Mamm. Genome. 2002;13:169–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

