A structural model for monastrol inhibition of dimeric kinesin Eg5
- PMID: 16642039
- PMCID: PMC1462975
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601108
A structural model for monastrol inhibition of dimeric kinesin Eg5
Abstract
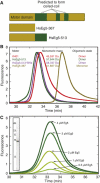
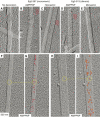
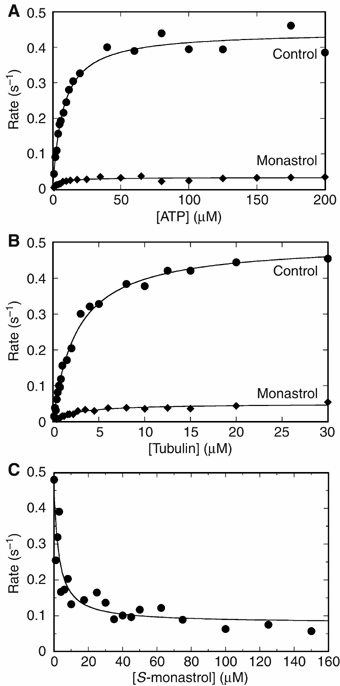
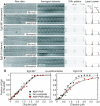
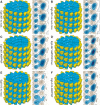
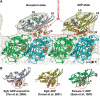
Eg5 or KSP is a homotetrameric Kinesin-5 involved in centrosome separation and assembly of the bipolar mitotic spindle. Analytical gel filtration of purified protein and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) of unidirectional shadowed microtubule-Eg5 complexes have been used to identify the stable dimer Eg5-513. The motility assays show that Eg5-513 promotes robust plus-end-directed microtubule gliding at a rate similar to that of homotetrameric Eg5 in vitro. Eg5-513 exhibits slow ATP turnover, high affinity for ATP, and a weakened affinity for microtubules when compared to monomeric Eg5. We show here that the Eg5-513 dimer binds microtubules with both heads to two adjacent tubulin heterodimers along the same microtubule protofilament. Under all nucleotide conditions tested, there were no visible structural changes in the monomeric Eg5-microtubule complexes with monastrol treatment. In contrast, there was a substantial monastrol effect on dimeric Eg5-513, which reduced microtubule lattice decoration. Comparisons between the X-ray structures of Eg5-ADP and Eg5-ADP-monastrol with rat kinesin-ADP after docking them into cryo-EM 3-D scaffolds revealed structural evidence for the weaker microtubule-Eg5 interaction in the presence of monastrol.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Monastrol inhibition of the mitotic kinesin Eg5.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 1;280(13):12658-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413140200. Epub 2005 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15665380 Free PMC article.
-
Disparity in allosteric interactions of monastrol with Eg5 in the presence of ADP and ATP: a difference FT-IR investigation.Biochemistry. 2004 Aug 10;43(31):9939-49. doi: 10.1021/bi048982y. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15287721
-
Interaction of the mitotic inhibitor monastrol with human kinesin Eg5.Biochemistry. 2003 Jan 21;42(2):338-49. doi: 10.1021/bi026716j. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12525161
-
Eg5 targeting agents: From new anti-mitotic based inhibitor discovery to cancer therapy and resistance.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Feb;184:114364. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114364. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33310050 Review.
-
Kinesin, 30 years later: Recent insights from structural studies.Protein Sci. 2015 Jul;24(7):1047-56. doi: 10.1002/pro.2697. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 25975756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kar3Vik1, a member of the kinesin-14 superfamily, shows a novel kinesin microtubule binding pattern.J Cell Biol. 2012 Jun 25;197(7):957-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201201132. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22734002 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic kinesin CENP-E promotes microtubule plus-end elongation.Curr Biol. 2010 Sep 28;20(18):1648-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.08.001. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20797864 Free PMC article.
-
ATPase cycle of the nonmotile kinesin NOD allows microtubule end tracking and drives chromosome movement.Cell. 2009 Jan 9;136(1):110-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.048. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19135893 Free PMC article.
-
Single-walled carbon nanotube-induced mitotic disruption.Mutat Res. 2012 Jun 14;745(1-2):28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.11.017. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 22178868 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of Polar versus Nematic Organization in Networks of Dynamic Microtubules and Mitotic Motors.Cell. 2018 Oct 18;175(3):796-808.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.029. Cell. 2018. PMID: 30340043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beuron F, Hoenger A (2001) Structural analysis of the microtubule–kinesin complex by cryo-electron microscopy. Methods Mol Biol 164: 235–254 - PubMed
-
- Blangy A, Lane HA, d'Herin P, Harper M, Kress M, Nigg EA (1995) Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 regulates spindle association of human Eg5, a kinesin-related motor essential for bipolar spindle formation in vivo. Cell 83: 1159–1169 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

