Specific RNA binding to ordered phospholipid bilayers
- PMID: 16641318
- PMCID: PMC1449910
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl220
Specific RNA binding to ordered phospholipid bilayers
Abstract
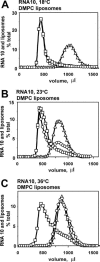
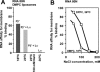
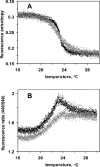
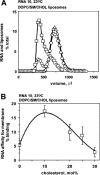
We have studied RNA binding to vesicles bounded by ordered and disordered phospholipid membranes. A positive correlation exists between bilayer order and RNA affinity. In particular, structure-dependent RNA binding appears for rafted (liquid-ordered) domains in sphingomyelin-cholesterol-1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine vesicles. Binding to more highly ordered gel phase membranes is stronger, but much less RNA structure-dependent. All modes of RNA-membrane association seem to be electrostatic and headgroup directed. Fluorometry on 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine liposomes indicates that bound RNA broadens the gel-fluid melting transition, and reduces lipid headgroup order, as detected via fluorometric measurement of intramembrane electric fields. RNA preference for rafted lipid was visualized and confirmed using multiple fluorophores that allow fluorescence and fluorescence resonance energy transfer microscopy on RNA molecules closely associated with ordered lipid patches within giant vesicles. Accordingly, both RNA structure and membrane order could modulate biological RNA-membrane interactions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A correlation between lipid domain shape and binary phospholipid mixture composition in free standing bilayers: A two-photon fluorescence microscopy study.Biophys J. 2000 Jul;79(1):434-47. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76305-3. Biophys J. 2000. PMID: 10866969 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the structure of lipids favoring disordered domain formation on the stability of cholesterol-containing ordered domains (lipid rafts): identification of multiple raft-stabilization mechanisms.Biophys J. 2007 Dec 15;93(12):4307-18. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.114967. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17766350 Free PMC article.
-
Combining fluorescence lifetime and polarization microscopy to discriminate phase separated domains in giant unilamellar vesicles.Biophys J. 2008 Dec 15;95(12):5737-47. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.108.131490. Epub 2008 Sep 12. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18790852 Free PMC article.
-
The polar nature of 7-ketocholesterol determines its location within membrane domains and the kinetics of membrane microsolubilization by apolipoprotein A-I.Biochemistry. 2005 Aug 2;44(30):10423-33. doi: 10.1021/bi0506425. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16042420
-
Transbilayer movement of phospholipids in biogenic membranes.Biochemistry. 2004 Mar 16;43(10):2673-81. doi: 10.1021/bi036200f. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15005602 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational change of single-stranded RNAs induced by liposome binding.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Nov 1;39(20):8891-900. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr568. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21785134 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of Membrane RNA Aptamers to Amyloid Beta Peptide: Implications for Exosome-Based Antioxidant Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 13;20(2):299. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020299. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30642129 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of extracellular vesicle-associated non-coding RNAs in hypoxia: Insights from cancer, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.Theranostics. 2022 Jul 18;12(13):5776-5802. doi: 10.7150/thno.73931. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35966580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNAs: reflecting or affecting cardiovascular disease?Curr Hypertens Rep. 2012 Dec;14(6):498-509. doi: 10.1007/s11906-012-0310-7. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2012. PMID: 22996205 Review.
-
Membrane transport in primitive cells.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Aug;2(8):a002188. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002188. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20679338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lewis R.N.A.H., McElhaney R.N. The mesomorphic phase behavior of lipid bilayers. In: Yeagle P.L., editor. The structure of biological membrane. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2005. pp. 53–120.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

