Lung dysfunction causes systemic hypoxia in estrogen receptor beta knockout (ERbeta-/-) mice
- PMID: 16636272
- PMCID: PMC1459034
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0602194103
Lung dysfunction causes systemic hypoxia in estrogen receptor beta knockout (ERbeta-/-) mice
Abstract
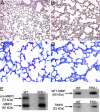
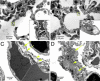
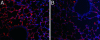
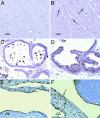
Estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) is highly expressed in both type I and II pneumocytes as well as bronchiolar epithelial cells. ERalpha is not detectable in the adult lung. Lungs of adult female ERbeta knockout (ERbeta-/-) mice have already been reported to have fewer alveoli and reduced elastic recoil. In this article, we report that, by 5 months of age, there are large areas of unexpanded alveoli in lungs of both male and female ERbeta-/- mice. There is increased staining for collagen and, by EM, abnormal clusters of collagen fibers are seen in the alveolar septa of ERbeta-/- mice. Immunohistochemical analysis and Western blotting with lung membrane fractions of ERbeta-/- mice revealed down-regulation of caveolin-1, increased expression of membrane type-1 metalloproteinase, matrix metalloproteinase 2 (active form), and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 2. Hypoxia, measured by immunohistochemical analysis for hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and chemical adducts (with Hypoxyprobe), was evident in the heart, ventral prostate, periovarian sac, kidney, liver, and brain of ERbeta-/- mice under resting conditions. Furthermore, both male and female adult ERbeta-/- mice were reluctant to run on a treadmill and tissue hypoxia became very pronounced after exercise. We conclude that ERbeta is necessary for the maintenance of the extracellular matrix composition in the lung and loss of ERbeta leads to abnormal lung structure and systemic hypoxia. Systemic hypoxia may be responsible for the reported left and right heart ventricular hypertrophy and systemic hypertension in ERbeta-/- mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: In addition to the partial funding of this study from Karo Bio AB, J.-Å.G. is a cofounder, deputy board member, stockholder, and consultant of Karo Bio AB.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective action of raloxifene against hypoxia-induced damage in mouse hippocampal cells depends on ERα but not ERβ or GPR30 signalling.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Feb;146:26-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 May 17. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 24846829
-
17β-Estradiol and/or Estrogen Receptor β Attenuate the Autophagic and Apoptotic Effects Induced by Prolonged Hypoxia Through HIF-1α-Mediated BNIP3 and IGFBP-3 Signaling Blockage.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(1):274-84. doi: 10.1159/000374070. Epub 2015 May 4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25967966
-
Estrogen-induced upregulation of Sftpb requires transcriptional control of neuregulin receptor ErbB4 in mouse lung type II epithelial cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Oct;1813(10):1717-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.06.020. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21777626 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Eralpha and ERbeta in the prostate: insights from genetic models and isoform-selective ligands.Ernst Schering Found Symp Proc. 2006;(1):131-47. doi: 10.1007/2789_2006_020. Ernst Schering Found Symp Proc. 2006. PMID: 17824175 Review.
-
Estrogen receptor β: the guardian of the endometrium.Hum Reprod Update. 2015 Mar-Apr;21(2):174-93. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmu053. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Hum Reprod Update. 2015. PMID: 25305176 Review.
Cited by
-
A role for estrogen receptor-α and estrogen receptor-β in collagen biosynthesis in mouse skin.J Invest Dermatol. 2013 Jan;133(1):120-7. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.264. Epub 2012 Aug 16. J Invest Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 22895361 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring estrogenic activity in lung cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2017 Feb;44(1):35-50. doi: 10.1007/s11033-016-4086-8. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Mol Biol Rep. 2017. PMID: 27783191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway up-regulates estrogen receptor-beta expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Jul;25(7):1145-58. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0495. Epub 2011 May 5. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21546410 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogens mediate cardiac hypertrophy in a stimulus-dependent manner.Endocrinology. 2012 Sep;153(9):4480-90. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1353. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22759381 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-activated cytotoxic agent tirapazamine enhances hepatic artery ligation-induced killing of liver tumor in HBx transgenic mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Oct 18;113(42):11937-11942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613466113. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27702890 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

