Quantitative real-time PCR protocol for analysis of nuclear receptor signaling pathways
- PMID: 16604184
- PMCID: PMC1402222
- DOI: 10.1621/nrs.01012
Quantitative real-time PCR protocol for analysis of nuclear receptor signaling pathways
Abstract
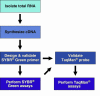
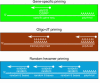
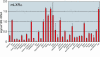
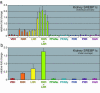
A major goal of the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas (NURSA) is to elucidate the biochemical and physiological roles of nuclear receptors in vivo. Characterizing the tissue expression pattern of individual receptors and their target genes in whole animals under various pharmacological conditions and genotypes is an essential component of this aim. Here we describe a high-throughput quantitative, real-time, reverse-transcription PCR (QPCR) method for the measurement of both the relative level of expression of a particular transcript in a given tissue or cell type, and the relative change in expression of a particular transcript after pharmacologic or genotypic manipulation. This method is provided as a standardized protocol for those in the nuclear receptor field. It is meant to be a simplified, easy to use protocol for the rapid, high-throughput measurement of transcript levels in a large number of samples. A subsequent report will provide validated primer and probe sequence information for the entire mouse and human nuclear receptor superfamily.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas (www.nursa.org): hyperlinking the nuclear receptor signaling community.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D221-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj029. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16381851 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: Evolution of NURSA, the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jun;23(6):740-6. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0135. Epub 2009 May 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19423650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas: development of a functional atlas of nuclear receptors.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Oct;19(10):2433-6. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0461. Epub 2005 Jul 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 16051673
-
Nuclear receptor atlas of female mouse liver parenchymal, endothelial, and Kupffer cells.Physiol Genomics. 2013 Apr 1;45(7):268-75. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00151.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Physiol Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23362145
-
[Quantitative PCR in the diagnosis of Leishmania].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):163-7. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305709 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
The interplay between chondrocyte redifferentiation pellet size and oxygen concentration.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058865. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554943 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating the ARNT/TACC3 axis: multiple approaches to manipulating protein/protein interactions with small molecules.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Mar 15;8(3):626-35. doi: 10.1021/cb300604u. Epub 2012 Dec 26. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23240775 Free PMC article.
-
Bulk and single-cell transcriptomics identify gene signatures of stem cell-derived NK cell donors with superior cytolytic activity.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;32(4):200870. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200870. eCollection 2024 Dec 19. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39346765 Free PMC article.
-
The master transcription factor SOX2, mutated in anophthalmia/microphthalmia, is post-transcriptionally regulated by the conserved RNA-binding protein RBM24 in vertebrate eye development.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Mar 13;29(4):591-604. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz278. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 31814023 Free PMC article.
-
DCIR and its ligand asialo-biantennary N-glycan regulate DC function and osteoclastogenesis.J Exp Med. 2021 Dec 6;218(12):e20210435. doi: 10.1084/jem.20210435. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34817551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Technotes Newsletter. Vol. 8. Ambion; 2001. The Top 10 Most common quantitative PCR pitfalls.
-
- Applied Biosystems: 1997. Relative Quantitation Of Gene Expression: ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: User Bulletin #2: Rev B.
-
- Applied Biosystems: 2001. ABI Prism 7900HT User Manual.
-
- Applied Biosystems; 2003. Essentials of Real Time PCR.
-
- Morrison T. B., Weis J. J., Wittwer C. T. Quantification of low-copy transcripts by continuous SYBR Green I monitoring during amplification. Biotechniques. 1998;24:954–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

