Inhibition of TRPM2 cation channels by N-(p-amylcinnamoyl)anthranilic acid
- PMID: 16604090
- PMCID: PMC1751561
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706739
Inhibition of TRPM2 cation channels by N-(p-amylcinnamoyl)anthranilic acid
Abstract
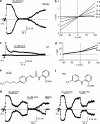
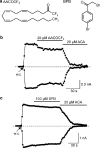
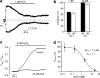
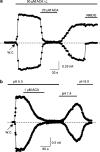
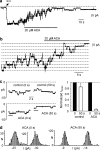
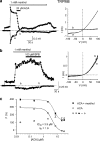
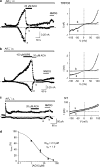
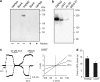
1. TRPM2 is a Ca2+ -permeable nonselective cation channel activated by intracellular ADP-ribose (ADPR) and by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). We investigated the modulation of TRPM2 activity by N-(p-amylcinnamoyl)anthranilic acid (ACA). ACA has previously been reported to inhibit phospholipase A2 (PLA2). 2. Using patch-clamp and calcium-imaging techniques, we show that extracellular application of 20 microM ACA completely blocked ADPR-induced whole-cell currents and H2O2-induced Ca2+ signals (IC50 = 1.7 microM) in HEK293 cells transfected with human TRPM2. Two other PLA2 inhibitors, p-bromophenacyl bromide (BPB; 100 microM) and arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone (20 microM), had no significant effect on ADPR-stimulated TRPM2 activity. 3. Inhibition of TRPM2 whole-cell currents by ACA was voltage independent and accelerated at decreased pH. ACA was ineffective when applied intracellularly. The single-channel conductance was not changed during ACA treatment, suggesting a reduction of TRPM2 open probability by modulating channel gating. 4. ACA (20 microM) also blocked currents through human TRPM8 and TRPC6 expressed in HEK293 cells, while BPB (100 microM) was ineffective. TRPC6-mediated currents (IC50 = 2.3 microM) and TRPM8-induced Ca2+ signals (IC50 = 3.9 microM) were blocked in a concentration-dependent manner. 5. ADPR-induced currents in human U937 cells, endogeneously expressing TRPM2 protein, were fully suppressed by 20 microM ACA. 6. Our data indicate that ACA modulates the activity of different TRP channels independent of PLA2 inhibition. Owing to its high potency and efficacy ACA can serve, in combination with other blockers, as a useful tool for studying the unknown function of TRPM2 in native cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitors of TRP channels reveal stimulus-dependent differential activation of Ca2+ influx pathways in human neutrophil granulocytes.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;380(6):497-507. doi: 10.1007/s00210-009-0464-2. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19894037
-
Inhibition of the transient receptor potential cation channel TRPM2 by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB).Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;153(6):1324-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707675. Epub 2008 Jan 21. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18204483 Free PMC article.
-
N-(p-amylcinnamoyl)anthranilic acid (ACA): a phospholipase A(2) inhibitor and TRP channel blocker.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2007 Spring;25(1):61-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2007.00005.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2007. PMID: 17445088 Review.
-
TRPM2 channel membrane currents in primary rat megakaryocytes were activated by the agonist ADP-ribose but not oxidative stress.J Membr Biol. 2011 May;241(2):51-7. doi: 10.1007/s00232-011-9356-8. Epub 2011 Apr 22. J Membr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21512734
-
TRPM2 cation channels, oxidative stress and neurological diseases: where are we now?Neurochem Res. 2011 Mar;36(3):355-66. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0347-4. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21140288 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological modulation of diacylglycerol-sensitive TRPC3/6/7 channels.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011 Jan 1;12(1):35-41. doi: 10.2174/138920111793937943. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20932261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A residue in the TRPM2 channel outer pore is crucial in determining species-dependent sensitivity to extracellular acidic pH.Pflugers Arch. 2011 Aug;462(2):293-302. doi: 10.1007/s00424-011-0957-y. Epub 2011 Apr 20. Pflugers Arch. 2011. PMID: 21505784
-
Identification of pore residues engaged in determining divalent cationic permeation in transient receptor potential melastatin subtype channel 2.J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 10;283(41):27426-27432. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801049200. Epub 2008 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18687688 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione Depletion and Parkinsonian Neurotoxin MPP+-Induced TRPM2 Channel Activation Play Central Roles in Oxidative Cytotoxicity and Inflammation in Microglia.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Aug;57(8):3508-3525. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01974-7. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32535761
-
Selective inhibition of TRPM2 channel by two novel synthesized ADPR analogues.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018 Feb;91(2):552-566. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13119. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018. PMID: 29034580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FLEIG A., PENNER R. The TRPM ion channel subfamily: molecular, biophysical and functional features. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004;25:633–639. - PubMed
-
- FONFRIA E., MARSHALL I.C., BOYFIELD I., SKAPER S.D., HUGHES J.P., OWEN D.E., ZHANG W., MILLER B.A., BENHAM C.D., MCNULTY S. Amyloid beta-peptide(1-42) and hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity are mediated by TRPM2 in rat primary striatal cultures. J. Neurochem. 2005;95:715–723. - PubMed
-
- GRIMM C., KRAFT R., SAUERBRUCH S., SCHULTZ G., HARTENECK C. Molecular and functional characterization of the melastatin-related cation channel TRPM3. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:21493–21501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

