Chemical modulation of receptor signaling inhibits regenerative angiogenesis in adult zebrafish
- PMID: 16565716
- PMCID: PMC1534118
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio778
Chemical modulation of receptor signaling inhibits regenerative angiogenesis in adult zebrafish
Abstract
We examined the role of angiogenesis and the need for receptor signaling using chemical inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor in the adult zebrafish tail fin. Using a small-molecule inhibitor, we were able to exert precise control over blood vessel regeneration. An angiogenic limit to tissue regeneration was determined, as avascular tissue containing skin, pigment, neuronal axons and bone precursors could regenerate up to about 1 mm. This indicates that tissues can regenerate without direct interaction with endothelial cells and at a distance from blood supply. We also investigated whether the effects of chemical inhibition could be enhanced in zebrafish vascular mutants. We found that adult zebrafish, heterozygous for a mutation in the critical receptor effector phospholipase Cgamma1, show a greater sensitivity to chemical inhibition. This study illustrates the utility of the adult zebrafish as a new model system for receptor signaling and chemical biology.
Figures

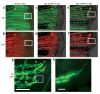

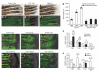
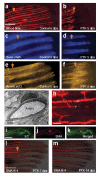
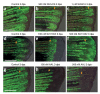
Comment in
-
Fishing and frogging for anti-angiogenic drugs.Nat Chem Biol. 2006 May;2(5):228-9. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0506-228. Nat Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 16619017 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Decreases Regenerative Angiogenesis in Axolotls.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017 Dec;300(12):2273-2280. doi: 10.1002/ar.23689. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 28921926 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical approaches to angiogenesis in development and regeneration.Methods Cell Biol. 2011;101:181-95. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387036-0.00008-6. Methods Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21550444 Review.
-
Quantitative assessment of the regenerative and mineralogenic performances of the zebrafish caudal fin.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 19;6:39191. doi: 10.1038/srep39191. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27991522 Free PMC article.
-
von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor mutants faithfully model pathological hypoxia-driven angiogenesis and vascular retinopathies in zebrafish.Dis Model Mech. 2010 May-Jun;3(5-6):343-53. doi: 10.1242/dmm.004036. Epub 2010 Mar 24. Dis Model Mech. 2010. PMID: 20335444
-
Modulation of VEGF signalling output by the Notch pathway.Bioessays. 2008 Apr;30(4):303-13. doi: 10.1002/bies.20736. Bioessays. 2008. PMID: 18348190 Review.
Cited by
-
Axitinib blocks Wnt/β-catenin signaling and directs asymmetric cell division in cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 16;113(33):9339-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604520113. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27482107 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule screening in zebrafish: an in vivo approach to identifying new chemical tools and drug leads.Cell Commun Signal. 2010 Jun 12;8:11. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-8-11. Cell Commun Signal. 2010. PMID: 20540792 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal occlusion uniformly partitions red blood cells fluxes within a microvascular network.PLoS Comput Biol. 2017 Dec 15;13(12):e1005892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005892. eCollection 2017 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 29244812 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical genetics suggests a critical role for lysyl oxidase in zebrafish notochord morphogenesis.Mol Biosyst. 2007 Jan;3(1):51-9. doi: 10.1039/b613673g. Epub 2006 Nov 14. Mol Biosyst. 2007. PMID: 17216056 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic effects of oridonin.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Apr 4;17(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1706-3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28376864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chanda SK. Fulfilling the promise: drug discovery in the post-genomic era. Drug Discov. Today. 2003;8:168–174. - PubMed
-
- Drews J. Drug discovery: a historical perspective. Science. 2000;287:1960–1964. - PubMed
-
- Lenz GR. Chemical ligands, genomics, and drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today. 2000;5:145–156. - PubMed
-
- Zon LI, Peterson RT. In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4:35–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

