Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs are evolutionarily conserved and differentially expressed
- PMID: 16557291
- PMCID: PMC1409806
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020023
Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs are evolutionarily conserved and differentially expressed
Abstract
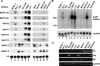
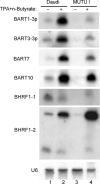
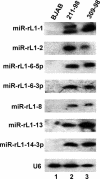
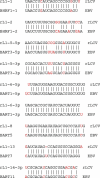
The pathogenic lymphocryptovirus Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is shown to express at least 17 distinct microRNAs (miRNAs) in latently infected cells. These are arranged in two clusters: 14 miRNAs are located in the introns of the viral BART gene while three are located adjacent to BHRF1. The BART miRNAs are expressed at high levels in latently infected epithelial cells and at lower, albeit detectable, levels in B cells. In contrast to the tissue-specific expression pattern of the BART miRNAs, the BHRF1 miRNAs are found at high levels in B cells undergoing stage III latency but are essentially undetectable in B cells or epithelial cells undergoing stage I or II latency. Induction of lytic EBV replication was found to enhance the expression of many, but not all, of these viral miRNAs. Rhesus lymphocryptovirus, which is separated from EBV by > or =13 million years of evolution, expresses at least 16 distinct miRNAs, seven of which are closely related to EBV miRNAs. Thus, lymphocryptovirus miRNAs are under positive selection and are likely to play important roles in the viral life cycle. Moreover, the differential regulation of EBV miRNA expression implies distinct roles during infection of different human tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quantitative studies of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs provide novel insights into their regulation.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(2):996-1010. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01528-10. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21068248 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary conservation of primate lymphocryptovirus microRNA targets.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(3):1617-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02071-13. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24257599 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr Virus BART miRNA Cluster of the M81 Strain Modulates Multiple Functions in Primary B Cells.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Dec 22;11(12):e1005344. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005344. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26694854 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Viral and Host microRNAs in Immune Regulation of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Diseases.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 3;11:367. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00367. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32194570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Jun;26:52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24602823 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Virally Encoded Circular RNAs in the Pathogenicity of Human Oncogenic Viruses.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 20;12:657036. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.657036. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33959113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The microRNA Transcriptome of Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV).Open Virol J. 2012;6:38-48. doi: 10.2174/1874357901206010038. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Open Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22715351 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Limits the Accumulation of IPO7, an Essential Gene Product.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 16;12:643327. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.643327. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33664726 Free PMC article.
-
Infection of Epstein-Barr virus in a gastric carcinoma cell line induces anchorage independence and global changes in gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 12;109(24):9593-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1202910109. Epub 2012 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22647604 Free PMC article.
-
Key elements involved in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer and their network regulation.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Sep 21;18:146. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0637-5. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30258285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14 . Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart BJ, Stack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature. 2000;403:901–906. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, Choi H, Kim J, et al. The nuclear RNase III drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 2003;425:415–419. - PubMed
-
- Palatnik JF, Allen E, Wu X, Schommer C, Schwab R, et al. Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature. 2003;425:275–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

