Engineered antibody Fc variants with enhanced effector function
- PMID: 16537476
- PMCID: PMC1389705
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508123103
Engineered antibody Fc variants with enhanced effector function
Abstract
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, a key effector function for the clinical efficacy of monoclonal antibodies, is mediated primarily through a set of closely related Fcgamma receptors with both activating and inhibitory activities. By using computational design algorithms and high-throughput screening, we have engineered a series of Fc variants with optimized Fcgamma receptor affinity and specificity. The designed variants display >2 orders of magnitude enhancement of in vitro effector function, enable efficacy against cells expressing low levels of target antigen, and result in increased cytotoxicity in an in vivo preclinical model. Our engineered Fc regions offer a means for improving the next generation of therapeutic antibodies and have the potential to broaden the diversity of antigens that can be targeted for antibody-based tumor therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: G.A.L., W.D., S.K., O.V., J.S.P., L.H., C.C., H.S.C., A.E., S.C.Y., J.V., D.F.C., R.J.H., and B.I.D. are employees of Xencor. All commercial affiliations, financial interests, and patent-licensing arrangements that could be considered to pose a financial conflict of interest regarding the submitted article have been disclosed.
Figures
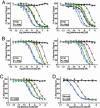

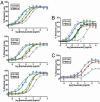
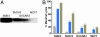
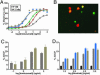

Similar articles
-
An engineered Fc variant of an IgG eliminates all immune effector functions via structural perturbations.Methods. 2014 Jan 1;65(1):114-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.06.035. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Methods. 2014. PMID: 23872058
-
Potent in vitro and in vivo activity of an Fc-engineered anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody against lymphoma and leukemia.Cancer Res. 2008 Oct 1;68(19):8049-57. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2268. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18829563
-
Combined Fc-protein- and Fc-glyco-engineering of scFv-Fc fusion proteins synergistically enhances CD16a binding but does not further enhance NK-cell mediated ADCC.J Immunol Methods. 2011 Oct 28;373(1-2):67-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.08.003. Epub 2011 Aug 9. J Immunol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21855548
-
A mechanistic perspective of monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy beyond target-related effects.Oncologist. 2007 Sep;12(9):1084-95. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-9-1084. Oncologist. 2007. PMID: 17914078 Review.
-
Engineering therapeutic monoclonal antibodies.Immunol Rev. 2008 Apr;222:9-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00601.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18363992 Review.
Cited by
-
Collective dynamics differentiates functional divergence in protein evolution.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(3):e1002428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002428. Epub 2012 Mar 29. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22479170 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Fc optimization to increase the cytotoxic activity of a CD19-targeting antibody.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 31;13:957874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.957874. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119088 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative evaluation of fucose reducing effects in a humanized antibody on Fcγ receptor binding and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activities.MAbs. 2012 May-Jun;4(3):326-40. doi: 10.4161/mabs.19941. Epub 2012 Apr 26. MAbs. 2012. PMID: 22531441 Free PMC article.
-
An antibody Fc engineered for conditional antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity at the low tumor microenvironment pH.J Biol Chem. 2022 Apr;298(4):101798. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101798. Epub 2022 Mar 3. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35248534 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of human FcgammaRI in mediating protection to malaria.PLoS Pathog. 2007 May 18;3(5):e72. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030072. PLoS Pathog. 2007. PMID: 17511516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiner L. M., Carter P. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:556–557. - PubMed
-
- Cohen-Solal J. F., Cassard L., Fridman W. H., Sautes-Fridman C. Immunol. Lett. 2004;92:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Jefferis R., Lund J. Immunol. Lett. 2002;82:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Raghavan M., Bjorkman P. J. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996;12:181–220. - PubMed
-
- Sondermann P., Kaiser J., Jacob U. J. Mol. Biol. 2001;309:737–749. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

