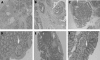
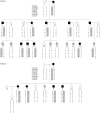
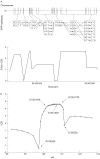
Mapping of hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome (HMPS) to chromosome 10q23 by genomewide high-density single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) scan and identification of BMPR1A loss of function
- PMID: 16525031
- PMCID: PMC2563243
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2005.034827
Mapping of hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome (HMPS) to chromosome 10q23 by genomewide high-density single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) scan and identification of BMPR1A loss of function
Abstract
Background: Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome (HMPS) is characterised by colonic polyps of mixed histological types that are autosomal dominantly inherited and eventually lead to colorectal cancer (CRC). Study of the molecular basis of HMPS will enhance our knowledge of the genetic basis of the mixed polyposis-carcinoma sequence in both hereditary and sporadic CRC.
Methods/results: We performed a genomewide linkage search on 15 members of a three-generation HMPS family using the GeneChip Human Mapping 10K Array and identified a 7 cM putative linkage interval on chromosome 10q23. Subsequently, 32 members from two HMPS families were typed with nine microsatellite markers spanning the region and the linkage was confirmed with a maximum multi-point logarithm of the odds (LOD) score of 4.6 (p<0.001). The 10q23.1-10q23.31 haplotypes segregate with the disease in both families. We screened for mutations in four candidate genes within the linkage region and identified an 11 bp deletion in the bone morphogenesis protein receptor 1A (BMPR1A) gene in one family.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that BMPR1A mutation accounts for HMPS. The data suggest that inactivating BMPR1A can initiate colorectal tumourigenesis via the mixed polyposis-carcinoma sequence.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none declared
Similar articles
-
Germline bone morphogenesis protein receptor 1A mutation causes colorectal tumorigenesis in hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome.Am J Gastroenterol. 2009 Dec;104(12):3027-33. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.542. Epub 2009 Sep 22. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19773747
-
Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome due to a BMPR1A mutation.Colorectal Dis. 2010 Jun;12(6):570-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2009.01931.x. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Colorectal Dis. 2010. PMID: 19438883
-
Genome-wide scan identifies a copy number variable region at 3q26 that regulates PPM1L in APC mutation-negative familial colorectal cancer patients.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010 Feb;49(2):99-106. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20724. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19847890
-
Mutations of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene in familial polyposis coli patients and sporadic colorectal tumors.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1991;22:285-92. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1991. PMID: 1668888 Review.
-
A review of juvenile polyposis syndrome.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Nov;20(11):1634-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.03865.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005. PMID: 16246179 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic architecture of colorectal cancer.Gut. 2015 Oct;64(10):1623-36. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306705. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Gut. 2015. PMID: 26187503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathology of the hereditary colorectal carcinoma.Fam Cancer. 2008;7(1):15-26. doi: 10.1007/s10689-007-9146-8. Epub 2007 Jun 13. Fam Cancer. 2008. PMID: 17564815 Review.
-
Clinical management of hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Feb;12(2):88-97. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.229. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25582351 Review.
-
A practice guideline from the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the National Society of Genetic Counselors: referral indications for cancer predisposition assessment.Genet Med. 2015 Jan;17(1):70-87. doi: 10.1038/gim.2014.147. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Genet Med. 2015. PMID: 25394175
-
The classification of intestinal polyposis.Nat Genet. 2013 Jan;45(1):2. doi: 10.1038/ng.2474. Nat Genet. 2013. PMID: 23268127 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bienz M, Clevers H. Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell 2000103311–320. - PubMed
-
- Schreibman I R, Baker M, Amos C, McGarrity T J. The hamartomatous polyposis syndromes: a clinical and molecular review. Am J Gastroenterol 2005100476–490. - PubMed
-
- Torlakovic E, Snover D C. Serrated adenomatous polyposis in humans. Gastroenterology 1996110748–755. - PubMed
-
- Jass J R, Whitehall V L, Young J, Leggett B A. Emerging concepts in colorectal neoplasia. Gastroenterology 2002123862–876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases