Human tissue-engineered blood vessels for adult arterial revascularization
- PMID: 16491087
- PMCID: PMC1513140
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1364
Human tissue-engineered blood vessels for adult arterial revascularization
Abstract
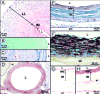
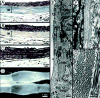
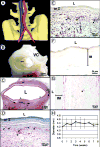
There is a crucial need for alternatives to native vein or artery for vascular surgery. The clinical efficacy of synthetic, allogeneic or xenogeneic vessels has been limited by thrombosis, rejection, chronic inflammation and poor mechanical properties. Using adult human fibroblasts extracted from skin biopsies harvested from individuals with advanced cardiovascular disease, we constructed tissue-engineered blood vessels (TEBVs) that serve as arterial bypass grafts in long-term animal models. These TEBVs have mechanical properties similar to human blood vessels, without relying upon synthetic or exogenous scaffolding. The TEBVs are antithrombogenic and mechanically stable for 8 months in vivo. Histological analysis showed complete tissue integration and formation of vasa vasorum. The endothelium was confluent and positive for von Willebrand factor. A smooth muscle-specific alpha-actin-positive cell population developed within the TEBV, suggesting regeneration of a vascular media. Electron microscopy showed an endothelial basement membrane, elastogenesis and a complex collagen network. These results indicate that a completely biological and clinically relevant TEBV can be assembled exclusively from an individual's own cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vascular smooth muscle enhances functionality of tissue-engineered blood vessels in vivo.J Vasc Surg. 2011 Feb;53(2):426-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.07.054. J Vasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 20934837
-
The development of a tissue-engineered artery using decellularized scaffold and autologous ovine mesenchymal stem cells.Biomaterials. 2010 Jan;31(2):296-307. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.049. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 19819544
-
Manipulation of remodeling pathways to enhance the mechanical properties of a tissue engineered blood vessel.J Biomech Eng. 2002 Dec;124(6):724-33. doi: 10.1115/1.1519278. J Biomech Eng. 2002. PMID: 12596641
-
Bioengineered blood vessels.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014 Apr;14(4):403-10. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2014.880419. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24460430 Review.
-
Cardiovascular tissue engineering: state of the art.Pathol Biol (Paris). 2005 Dec;53(10):599-612. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2004.12.006. Epub 2005 Jan 25. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2005. PMID: 16364812 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological matrices and bionanotechnology.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2007 Aug 29;362(1484):1313-20. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2117. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17581810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitigating challenges and expanding the future of vascular tissue engineering-are we there yet?Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 4;13:1079421. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1079421. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36685187 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pulmonary artery augmentation and aortic valve repair using novel tissue-engineered grafts.JTCVS Tech. 2022 Jan 21;12:143-152. doi: 10.1016/j.xjtc.2021.09.058. eCollection 2022 Apr. JTCVS Tech. 2022. PMID: 35403062 Free PMC article.
-
The Evolution of Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft Technologies: From Preclinical Trials to Advancing Patient Care.Appl Sci (Basel). 2019 Apr;9(7):1274. doi: 10.3390/app9071274. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Appl Sci (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31890320 Free PMC article.
-
New methods to diagnose and treat cartilage degeneration.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009 Nov;5(11):599-607. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.204. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19786989 Review.
References
-
- Weinberg CB, Bell E. A blood vessel model constructed from collagen and cultured vascular cells. Science. 1986;231:397–400. - PubMed
-
- Niklason LE, et al. Functional arteries grown in vitro. Science. 1999;284:489–93. - PubMed
-
- Chue WL, et al. Dog peritoneal and pleural cavities as bioreactors to grow autologous vascular grafts. J Vasc Surg. 2004;39:859–867. - PubMed
-
- Kakisis JD, Liapis CD, Breuer C, Sumpio BE. Artificial blood vessel: the Holy Grail of peripheral vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg. 2005;41:349–54. - PubMed
-
- L’Heureux N, Germain L, Labbe R, Auger FA. In vitro construction of a human blood vessel from cultured vascular cells: a morphologic study. Journal of Vascular Surgery. 1993;17:499–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

