A hyper-dynamic equilibrium between promoter-bound and nucleoplasmic dimers controls NF-kappaB-dependent gene activity
- PMID: 16467852
- PMCID: PMC1383558
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600977
A hyper-dynamic equilibrium between promoter-bound and nucleoplasmic dimers controls NF-kappaB-dependent gene activity
Abstract
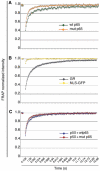
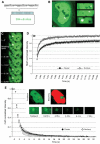
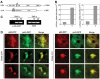
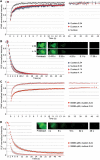
Because of its very high affinity for DNA, NF-kappaB is believed to make long-lasting contacts with cognate sites and to be essential for the nucleation of very stable enhanceosomes. However, the kinetic properties of NF-kappaB interaction with cognate sites in vivo are unknown. Here, we show that in living cells NF-kappaB is immobilized onto high-affinity binding sites only transiently, and that complete NF-kappaB turnover on active chromatin occurs in less than 30 s. Therefore, promoter-bound NF-kappaB is in dynamic equilibrium with nucleoplasmic dimers; promoter occupancy and transcriptional activity oscillate synchronously with nucleoplasmic NF-kappaB and independently of promoter occupancy by other sequence-specific transcription factors. These data indicate that changes in the nuclear concentration of NF-kappaB directly impact on promoter function and that promoters sample nucleoplasmic levels of NF-kappaB over a timescale of seconds, thus rapidly re-tuning their activity. We propose a revision of the enhanceosome concept in this dynamic framework.
Figures

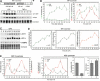
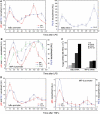
Similar articles
-
One nucleotide in a kappaB site can determine cofactor specificity for NF-kappaB dimers.Cell. 2004 Aug 20;118(4):453-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.007. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15315758
-
In vivo binding of NF-kappaB to the IkappaBbeta promoter is insufficient for transcriptional activation.Biochem J. 2006 Nov 15;400(1):115-25. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060786. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16792530 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent biphasic induction and transcriptional activity of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) in EA.hy.926 endothelial cells after low-dose X-irradiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2004 Feb;80(2):115-23. doi: 10.1080/09553000310001654701. Int J Radiat Biol. 2004. PMID: 15164793
-
Transcriptional regulation via the NF-kappaB signaling module.Oncogene. 2006 Oct 30;25(51):6706-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209933. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 17072323 Review.
-
Interactions of NF-kappaB with chromatin: the art of being at the right place at the right time.Nat Immunol. 2005 May;6(5):439-45. doi: 10.1038/ni1196. Nat Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15843800 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factor oscillations induce differential gene expressions.Biophys J. 2012 Jun 6;102(11):2413-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.04.023. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22713556 Free PMC article.
-
First Responders Shape a Prompt and Sharp NF-κB-Mediated Transcriptional Response to TNF-α.iScience. 2020 Sep 4;23(9):101529. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101529. eCollection 2020 Sep 25. iScience. 2020. PMID: 33083759 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Mechanism of Transcriptional Bursting: A Technical Resolution-Independent Study.Biology (Basel). 2020 Oct 19;9(10):339. doi: 10.3390/biology9100339. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33086528 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitination of NF-κB by Ubiquitin-Specific Protease-7 promotes transcription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 8;110(2):618-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208446110. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23267096 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk in inflammation: the interplay of glucocorticoid receptor-based mechanisms and kinases and phosphatases.Endocr Rev. 2009 Dec;30(7):830-82. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0013. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Endocr Rev. 2009. PMID: 19890091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

