Integrins control dendritic spine plasticity in hippocampal neurons through NMDA receptor and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-mediated actin reorganization
- PMID: 16467530
- PMCID: PMC6793632
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4091-05.2006
Integrins control dendritic spine plasticity in hippocampal neurons through NMDA receptor and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-mediated actin reorganization
Abstract
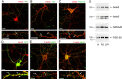
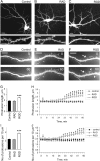
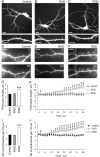
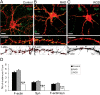
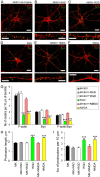
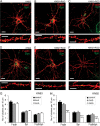
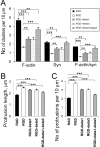
The formation of dendritic spines during development and their structural plasticity in the adult brain are critical aspects of synaptogenesis and synaptic plasticity. Many different factors and proteins have been shown to control dendritic spine development and remodeling (Ethell and Pasquale, 2005). The extracellular matrix (ECM) components and their cell surface receptors, integrins, have been found in the vicinity of synapses and shown to regulate synaptic efficacy and play an important role in long-term potentiation (Bahr et al., 1997; Chavis and Westbrook, 2001; Chan et al., 2003; Lin et al., 2003; Bernard-Trifilo et al., 2005). Although molecular mechanisms by which integrins affect synaptic efficacy have begun to emerge, their role in structural plasticity is poorly understood. Here, we show that integrins are involved in spine remodeling in cultured hippocampal neurons. The treatment of 14 d in vitro hippocampal neurons with arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD)-containing peptide, an established integrin ligand, induced elongation of existing dendritic spines and promoted formation of new filopodia. These effects were also accompanied by integrin-dependent actin reorganization and synapse remodeling, which were partially inhibited by function-blocking antibodies against beta1 and beta3 integrins. This actin reorganization was blocked with the NMDA receptor (NMDAR) antagonist MK801 [(+)-5-methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5,10-imine hydrogen maleate]. The Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) inhibitor KN93 (N-[2-[N-(4-chlorocinnamyl)-N-methylaminomethyl]phenyl]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methoxybenzenesulfonamide) also suppressed RGD-induced actin reorganization and synapse remodeling. Our findings show that integrins control ECM-mediated spine remodeling in hippocampal neurons through NMDAR/CaMKII-dependent actin reorganization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influx of extracellular calcium regulates actin-dependent morphological plasticity in dendritic spines.Neuropharmacology. 2004 Oct;47(5):669-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.07.038. Neuropharmacology. 2004. PMID: 15458838
-
A model of NMDA receptor-mediated activity in dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1992 Dec;68(6):2248-59. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.6.2248. J Neurophysiol. 1992. PMID: 1337105 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic secretion of BDNF and NT-3 from hippocampal neurons depends on calcium calmodulin kinase II signaling and proceeds via delayed fusion pore opening.J Neurosci. 2007 Sep 26;27(39):10350-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0692-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17898207 Free PMC article.
-
Making of a Synapse: Recurrent Roles of Drebrin A at Excitatory Synapses Throughout Life.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1006:119-139. doi: 10.1007/978-4-431-56550-5_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28865018 Review.
-
The roles of CaMKII and F-actin in the structural plasticity of dendritic spines: a potential molecular identity of a synaptic tag?Physiology (Bethesda). 2009 Dec;24:357-66. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00029.2009. Physiology (Bethesda). 2009. PMID: 19996366 Review.
Cited by
-
EphB2 in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Regulates Vulnerability to Stress.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Sep;41(10):2541-56. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.58. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27103064 Free PMC article.
-
The CNS synapse revisited: gaps, adhesive welds, and borders.Neurochem Res. 2007 Feb;32(2):303-10. doi: 10.1007/s11064-006-9181-0. Epub 2006 Nov 2. Neurochem Res. 2007. PMID: 17080313 Review.
-
alpha5 integrin signaling regulates the formation of spines and synapses in hippocampal neurons.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 9;282(10):6929-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610981200. Epub 2007 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17213186 Free PMC article.
-
The Gliocentric Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 5;19(10):3033. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103033. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30301132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo roles for matrix metalloproteinase-9 in mature hippocampal synaptic physiology and plasticity.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Jul;98(1):334-44. doi: 10.1152/jn.00202.2007. Epub 2007 May 9. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17493927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK, Juliano RL (1998). Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol Rev 50:197–263. - PubMed
-
- Bernard-Trifilo JA, Kramar EA, Torp R, Lin CY, Pineda EA, Lynch G, Gall CM (2005). Integrin signaling cascades are operational in adult hippocampal synapses and modulate NMDA receptor physiology. J Neurochem 93:834–849. - PubMed
-
- Bi X, Lynch G, Zhou J, Gall CM (2001). Polarized distribution of alpha5 integrin in dendrites of hippocampal and cortical neurons. J Comp Neurol 435:184–193. - PubMed
-
- Blystone SD (2002). Kinetic regulation of beta 3 integrin tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 277:46886–46890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
