Progression of regulatory gene expression states in fetal and adult pro-T-cell development
- PMID: 16448545
- PMCID: PMC4157939
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00355.x
Progression of regulatory gene expression states in fetal and adult pro-T-cell development
Abstract
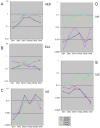
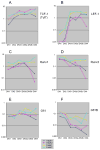
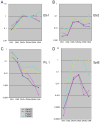
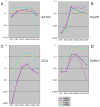
Precursors entering the T-cell developmental pathway traverse a progression of states characterized by distinctive patterns of gene expression. Of particular interest are regulatory genes, which ultimately control the dwell time of cells in each state and establish the mechanisms that propel them forward to subsequent states. Under particular genetic and developmental circumstances, the transitions between these states occur with different timing, and environmental feedbacks may shift the steady-state accumulations of cells in each state. The fetal transit through pro-T-cell stages is faster than in the adult and subject to somewhat different genetic requirements. To explore causes of such variation, this review presents previously unpublished data on differentiation gene activation in pro-T cells of pre-T-cell receptor-deficient mutant mice and a quantitative comparison of the profiles of transcription factor gene expression in pro-T-cell subsets of fetal and adult wildtype mice. Against a background of consistent gene expression, several regulatory genes show marked differences between fetal and adult expression profiles, including those encoding two basic helix-loop-helix antagonist Id factors, the Ets family factor SpiB and the Notch target gene Deltex1. The results also reveal global differences in regulatory alterations triggered by the first T-cell receptor-dependent selection events in fetal and adult thymopoiesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular dissection of prethymic progenitor entry into the T lymphocyte developmental pathway.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 1;179(1):421-38. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.421. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17579063
-
A novel role for HEB downstream or parallel to the pre-TCR signaling pathway during alpha beta thymopoiesis.J Immunol. 1999 Sep 15;163(6):3331-43. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10477603
-
At the crossroads: diverse roles of early thymocyte transcriptional regulators.Immunol Rev. 2006 Feb;209:191-211. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00352.x. Immunol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16448544 Review.
-
The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor HEBAlt is expressed in pro-T cells and enhances the generation of T cell precursors.J Immunol. 2006 Jul 1;177(1):109-19. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.1.109. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16785505
-
Transcriptional control of T-cell development.Int Immunol. 2011 Nov;23(11):661-8. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxr078. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Int Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21948191 Review.
Cited by
-
Mast cell lineage diversion of T lineage precursors by the essential T cell transcription factor GATA-3.Nat Immunol. 2007 Aug;8(8):845-55. doi: 10.1038/ni1486. Epub 2007 Jul 1. Nat Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17603486 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional establishment of cell-type identity: dynamics and causal mechanisms of T-cell lineage commitment.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013;78:31-41. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2013.78.020271. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013. PMID: 24135716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Action of Hematopoietic Transcription Factor PU.1 in Initiation of T-Cell Development.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 20;10:228. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00228. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30842770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch/Delta signaling constrains reengineering of pro-T cells by PU.1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 8;103(32):11993-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601188103. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16880393 Free PMC article.
-
GATA-3 is required for early T lineage progenitor development.J Exp Med. 2009 Dec 21;206(13):2987-3000. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090934. Epub 2009 Nov 23. J Exp Med. 2009. PMID: 19934022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rothenberg EV, Taghon T. Molecular Genetics of T Cell Development. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:601–49. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg EV, Anderson MK. Elements of transcription factor network design for T-lineage specification. Devel Biol. 2002;246:29–44. - PubMed
-
- Han H, Tanigaki K, Yamamoto N, Kuroda K, Yoshimoto M, Nakahata T, Ikuta K, Honjo T. Inducible gene knockout of transcription factor recombination signal binding protein-J reveals its essential role in T versus B lineage decision. Int Immunol. 2002;14:637–45. - PubMed
-
- Tanigaki K, Tsuji M, Yamamoto N, Han H, Tsukada J, Inoue H, Kubo M, Honjo T. Regulation of αβ/γδ T cell lineage commitment and peripheral T cell responses by Notch/RBP-J signaling. Immunity. 2004;20:611–22. - PubMed
-
- Maillard I, Weng AP, Carpenter AC, Rodriguez CG, Sai H, Xu L, Allman D, Aster JC, Pear WS. Mastermind critically regulates Notch-mediated lymphoid cell fate decisions. Blood. 2004;104:1696–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

