Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 incorporated with fusion proteins consisting of integrase and the designed polydactyl zinc finger protein E2C can bias integration of viral DNA into a predetermined chromosomal region in human cells
- PMID: 16439549
- PMCID: PMC1367172
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.4.1939-1948.2006
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 incorporated with fusion proteins consisting of integrase and the designed polydactyl zinc finger protein E2C can bias integration of viral DNA into a predetermined chromosomal region in human cells
Abstract
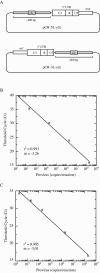
In vitro studies using fusion proteins consisting of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase (IN) and a synthetic polydactyl zinc finger protein E2C, a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein, showed that integration of retroviral DNA can be biased towards a contiguous 18-bp E2C-recognition site. To determine whether the fusion protein strategy can achieve site-specific integration in vivo, viruses were prepared by cotransfection and various IN-E2C fusion proteins were packaged in trans into virions. The resulting viruses incorporated with the IN-E2C fusion proteins were functional and capable of performing integration at a level ranging from 1 to 24% of that of viruses containing wild-type (WT) IN. Two of the more infectious viruses, which contained E2C fused to either the N (E2C/IN) or to the C (IN/E2C) terminus of IN, were tested for their ability to direct integration into a unique E2C-binding site present within the 5' untranslated region of erbB-2 gene on human chromosome 17. The copy number of proviral DNA was measured using a quantitative real-time nested-PCR assay, and the specificity of directed integration was determined by comparing the number of proviruses within the vicinity of the E2C-binding site to that in the whole genome. Viruses containing IN/E2C fusion proteins had sevenfold higher preference for integrating near the E2C-binding site than those viruses containing WT IN, whereas viruses containing E2C/IN had 10-fold higher preference. The results indicated that the IN-E2C fusion protein strategy is capable of directing integration of retroviral DNA into a predetermined chromosomal region in the human genome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Evaluating Different Types of Cancer Survivorship Care [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2019 Jul. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2019 Jul. PMID: 39602557 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an HIV reporter virus that identifies latently infected CD4+ T cells.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Jun 13;2(6):100238. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100238. eCollection 2022 Jun 20. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 35784650 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted gene insertion for molecular medicine.J Mol Med (Berl). 2008 Nov;86(11):1205-19. doi: 10.1007/s00109-008-0381-8. Epub 2008 Jul 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18607557 Review.
-
Driving DNA transposition by lentiviral protein transduction.Mob Genet Elements. 2014 Jun 23;4:e29591. doi: 10.4161/mge.29591. eCollection 2014. Mob Genet Elements. 2014. PMID: 25057443 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Latency in Primary Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages Induced by Sustained M1 Polarization.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 24;8(1):14249. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32451-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30250078 Free PMC article.
-
GCN5-dependent acetylation of HIV-1 integrase enhances viral integration.Retrovirology. 2010 Mar 12;7:18. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-18. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 20226045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. A., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1999. Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York, N.Y.
-
- Beerli, R. R., and C. F. Barbas III. 2002. Engineering polydactyl zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat. Biotechnol. 20:135-141. - PubMed
-
- Beerli, R. R., D. J. Segal, B. Dreier, and C. F. Barbas, III. 1998. Toward controlling gene expression at will: specific regulation of the erbB-2/HER-2 promoter by using polydactyl zinc finger proteins constructed from modular building blocks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:14628-14633. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blancafort, P., D. J. Segal, and C. F. Barbas III. 2004. Designing transcription factor architectures for drug discovery. Mol. Pharmacol. 66:1361-1371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

