Human TRPC6 expressed in HEK 293 cells forms non-selective cation channels with limited Ca2+ permeability
- PMID: 16439426
- PMCID: PMC1779672
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.103143
Human TRPC6 expressed in HEK 293 cells forms non-selective cation channels with limited Ca2+ permeability
Abstract
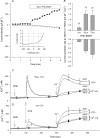
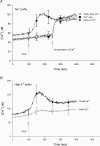
TRPC6 is thought to be a Ca(2+)-permeable cation channel activated following stimulation of G-protein-coupled membrane receptors linked to phospholipase C (PLC). TRPC6 current is also activated by exogenous application of 1-oleoyl-acetyl-sn-glycerol (OAG) or by inhibiting 1,2-diacylglycerol (DAG) lipase activity using RHC80267. In the present study, both OAG and RHC80267 increased whole-cell TRPC6 current in cells from a human embryonic kidney cell line (HEK 293) stably expressing TRPC6, but neither compound increased cytosolic free Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) when the cells were bathed in high-K(+) buffer to hold the membrane potential near 0 mV. These results suggested that TRPC6 channels have limited Ca(2+) permeability relative to monovalent cation permeability and/or that Ca(2+) influx via TRPC6 is greatly attenuated by depolarization. To evaluate Ca(2+) permeability, TRPC6 currents were examined in extracellular buffer in which Ca(2+) was varied from 0.02 to 20 mm. The results were consistent with a pore-permeation model in which Ca(2+) acts primarily as a blocking ion and contributes only a small percentage ( approximately 4%) to whole-cell currents in the presence of extracellular Na(+). Measurement of single-cell fura-2 fluorescence during perforated-patch recording of TRPC6 currents showed that OAG increased [Ca(2+)](i) 50-100 nm when the membrane potential was clamped at between -50 and -80 mV, but had little or no effect if the membrane potential was left uncontrolled. These results suggest that in cells exhibiting a high input resistance, the primary effect of activating TRPC6 will be membrane depolarization. However, in cells able to maintain a hyperpolarized potential (e.g. cells with a large inwardly rectifying or Ca(2+)-activated K(+) current), activation of TRPC6 will lead to a sustained increase in [Ca(2+)](i). Thus, the contribution of TRPC6 current to both the kinetics and magnitude of the Ca(2+) response will be cell specific and dependent upon the complement of other channel types.
Figures


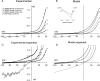
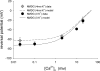
 ) as in Fig. 5 are plotted as a function of extracellular Ca2+ concentration (n = 3–17 for each data point). The lines drawn are the values predicted from the single-site pore model under each ionic condition.
) as in Fig. 5 are plotted as a function of extracellular Ca2+ concentration (n = 3–17 for each data point). The lines drawn are the values predicted from the single-site pore model under each ionic condition.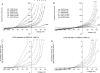


Similar articles
-
Diacylglycerol analogues activate second messenger-operated calcium channels exhibiting TRPC-like properties in cortical neurons.J Neurochem. 2009 Jan;108(1):126-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05752.x. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19094061
-
Angiotensin II activates two cation conductances with distinct TRPC1 and TRPC6 channel properties in rabbit mesenteric artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2006 Dec 1;577(Pt 2):479-95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.119305. Epub 2006 Sep 14. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16973707 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endogenous TRPC6 channels in Ca2+ signal generation in A7r5 smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 2;280(48):39786-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506064200. Epub 2005 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16204251
-
Store-Independent Orai Channels Regulated by STIM.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 11. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 11. PMID: 30299650 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
TRPC6.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007;(179):125-41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34891-7_7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17217054 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic target for nephrotic syndrome: Identification of novel slit diaphragm associated molecules.World J Nephrol. 2014 Aug 6;3(3):77-84. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v3.i3.77. World J Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 25332898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental changes of BKCa channels depend on differentiation status in cultured podocytes.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2013 Mar;49(3):205-11. doi: 10.1007/s11626-013-9590-8. Epub 2013 Feb 27. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2013. PMID: 23443253
-
The Effects of TRPC6 Knockout in Animal Models of Kidney Disease.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 18;12(11):1710. doi: 10.3390/biom12111710. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36421724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transmembrane insertases and N-glycosylation critically determine synthesis, trafficking, and activity of the nonselective cation channel TRPC6.J Biol Chem. 2019 Aug 23;294(34):12655-12669. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008299. Epub 2019 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31266804 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Targets for Stroke Therapy: Special Focus on TRPC Channels and TRPC6.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Mar 18;12:70. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00070. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32256338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnon A, Hamlyn JM, Blaustein MP. Ouabain augments Ca2+ transients in arterial smooth muscle without raising cytosolic Na+ Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:H679–H691. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay BC, Swaim WD, Liu X, Redman R, Patterson RL, Ambudkar IS. Apical localization of a functional TRPC3/TRPC6-Ca2+-signaling complex in polarized epithelial cells: role in apical Ca2+ influx. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:12908–12916. - PubMed
-
- Bleasdale JE, Thakur NR, Gremban RS, Bundy GL, Fitzpatrick FA, Smith RJ, Bunting S. Selective inhibition of receptor-coupled phospholipase C-dependent processes in human platelets and polymorphonuclear neutorphils. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990;255:756–768. - PubMed
-
- Boulay G, Zhu X, Peyton M, Hurst R, Stefani E, Birnbaumer L. Cloning and expression of a novel mammalain homolog of Drosophila transient receptor potential (Trp) involved in calcium entry secondary to activation of receptors coupled by Gq class of G protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29672–29680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

