Bone disorders in experimentally induced liver disease in growing rats
- PMID: 16437666
- PMCID: PMC4725093
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i45.7169
Bone disorders in experimentally induced liver disease in growing rats
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the change of bone parameters in a new model of experimentally induced liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in growing rats.
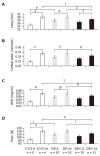
Methods: Fischer-344 rats (n = 55) were used. Carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)), phenobarbital (PB), and a single diethylnitrosamine (DEN) injection were used. Animals were killed at wk 8 and 16. Bone mineral content, femoral length, cortical index (quotient of cortical thickness and whole diameter) and ultimate bending load (F(max)) of the femora were determined. The results in animals treated with DEN+PB+CCl(4) (DPC, n = 21) were compared to those in untreated animals (UNT, n = 14) and in control group treated only with DEN+PB (DP, n = 20).
Results: Fatty liver and cirrhosis developed in each DPC-treated rat at wk 8 and HCC was presented at wk 16. No skeletal changes were found in this group at wk 8, but each parameter was lower (P<0.05 for each) at wk 16 in comparison to the control group. Neither fatty liver nor cirrhosis was observed in DP-treated animals at any time point. Femoral length and F(max) values were higher (P<0.05 for both) in DP-treated animals at wk 8 compared to the UNT controls. However, no difference was found at wk 16.
Conclusion: Experimental liver cirrhosis and HCC are accompanied with inhibited skeletal growth, reduced bone mass, and decreased mechanical resistance in growing rats. Our results are in concordance with the data of other studies using different animal models. A novel finding is the transiently accelerated skeletal growth and bone strength after a 8-wk long phenobarbital treatment following diethylnitrosamine injection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased hepatocarcinogenic effect of diethylnitrosamine in experimentally induced liver cirrhosis in rat: delay or inhibition?Cancer Lett. 1994 Apr 29;79(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(94)90055-8. Cancer Lett. 1994. PMID: 8187048
-
1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 prevents DNA damage and restores antioxidant enzymes in rat hepatocarcinogenesis induced by diethylnitrosamine and promoted by phenobarbital.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 May 1;10(9):1268-75. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i9.1268. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15112340 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory and promoting effects of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver cirrhosis on the diethylnitrosamine hepatocarcinogenesis in rats.Cancer Lett. 1991 Apr;57(1):67-73. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(91)90065-p. Cancer Lett. 1991. PMID: 2025881
-
Effects of dietary selenium concentration on the development of enzyme-altered liver foci and hepatocellular carcinoma induced by diethylnitrosamine or N-acetylaminofluorene in rats.Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 1):5489-95. Cancer Res. 1985. PMID: 2865004
-
Effects of IGF-I treatment on osteopenia in rats with advanced liver cirrhosis.J Physiol Biochem. 2000 Jun;56(2):91-9. doi: 10.1007/BF03179904. J Physiol Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11014614
Cited by
-
Hepatoprotective Effects of Silybum marianum (Silymarin) and Glycyrrhiza glabra (Glycyrrhizin) in Combination: A Possible Synergy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:641597. doi: 10.1155/2014/641597. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24795768 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse model of carbon tetrachloride induced liver fibrosis: Histopathological changes and expression of CD133 and epidermal growth factor.BMC Gastroenterol. 2010 Jul 9;10:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-79. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20618941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heathcote J. Osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 1999;1:455–458. - PubMed
-
- McCaughan GW, Feller RB. Osteoporosis in chronic liver disease: pathogenesis, risk factors, and management. Dig Dis. 1994;12:223–231. - PubMed
-
- Monegal A, Navasa M, Guanabens N, Peris P, Pons F, Martinez de Osaba MJ, Rimola A, Rodes J, Munoz-Gomez J. Osteoporosis and bone mineral metabolism disorders in cirrhotic patients referred for orthotopic liver transplantation. Calcif Tissue Int. 1997;60:148–154. - PubMed
-
- Corazza GR, Trevisani F, Di Stefano M, De Notariis S, Veneto G, Cecchetti L, Minguzzi L, Gasbarrini G, Bernardi M. Early increase of bone resorption in patients with liver cirrhosis secondary to viral hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2000;45:1392–1399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

