Direct ribosomal binding by a cellular inhibitor of translation
- PMID: 16429152
- PMCID: PMC2741086
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb1052
Direct ribosomal binding by a cellular inhibitor of translation
Abstract
During apoptosis and under conditions of cellular stress, several signaling pathways promote inhibition of cap-dependent translation while allowing continued translation of specific messenger RNAs encoding regulatory and stress-response proteins. We report here that the apoptotic regulator Reaper inhibits protein synthesis by binding directly to the 40S ribosomal subunit. This interaction does not affect either ribosomal association of initiation factors or formation of 43S or 48S complexes. Rather, it interferes with late initiation events upstream of 60S subunit joining, apparently modulating start-codon recognition during scanning. CrPV IRES-driven translation, involving direct ribosomal recruitment to the start site, is relatively insensitive to Reaper. Thus, Reaper is the first known cellular ribosomal binding factor with the potential to allow selective translation of mRNAs initiating at alternative start codons or from certain IRES elements. This function of Reaper may modulate gene expression programs to affect cell fate.
Figures
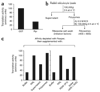
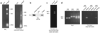
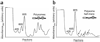
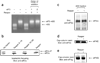
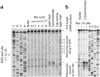
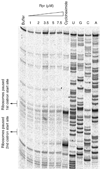
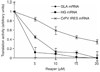
Comment in
-
Translation, interrupted.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Feb;13(2):98-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb0206-98. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16462810 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Internal ribosome entry site drives cap-independent translation of reaper and heat shock protein 70 mRNAs in Drosophila embryos.RNA. 2004 Nov;10(11):1783-97. doi: 10.1261/rna.7154104. RNA. 2004. PMID: 15496524 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of mammalian 48S ribosomal translation initiation complex.Methods Enzymol. 2007;430:179-208. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)30008-6. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17913639
-
Translation, interrupted.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Feb;13(2):98-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb0206-98. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16462810 No abstract available.
-
Translation initiation by factor-independent binding of eukaryotic ribosomes to internal ribosomal entry sites.C R Biol. 2005 Jul;328(7):589-605. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2005.02.004. C R Biol. 2005. PMID: 15992743 Review.
-
Structural Insights into the Mechanism of Scanning and Start Codon Recognition in Eukaryotic Translation Initiation.Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 Aug;42(8):589-611. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.03.004. Epub 2017 Apr 22. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28442192 Review.
Cited by
-
IRES Trans-Acting Factors, Key Actors of the Stress Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 20;20(4):924. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040924. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30791615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis of ribosomes: translational control of mRNA populations by glycogen synthase GYS1.J Mol Biol. 2011 Jul 1;410(1):118-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.04.064. Epub 2011 May 5. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21570405 Free PMC article.
-
Translation machinery reprogramming in programmed cell death in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Jan 18;7(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00392-x. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 33462193 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory lipid mediator 15d-PGJ2 inhibits translation through inactivation of eIF4A.EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5020-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601920. Epub 2007 Nov 22. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 18034160 Free PMC article.
-
Translatomics: The Global View of Translation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 8;20(1):212. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010212. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30626072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holcik M, Sonenberg N. Translational control in stress and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005;6:318–327. - PubMed
-
- Marash L, Kimchi A. DAP5 and IRES-mediated translation during programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:554–562. - PubMed
-
- Bushell M, et al. Cleavage of polypeptide chain initiation factor eIF4GI during apoptosis in lymphoma cells: characterisation of an internal fragment generated by caspase-3-mediated cleavage. Cell Death Differ. 2000;7:628–636. - PubMed
-
- Marissen WE, Gradi A, Sonenberg N, Lloyd RE. Cleavage of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4GII correlates with translation inhibition during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2000;7:1234–1243. - PubMed
-
- Sonenberg N, Dever TE. Eukaryotic translation initiation factors and regulators. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003;13:56–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

