Autoantibodies to myelin basic protein catalyze site-specific degradation of their antigen
- PMID: 16387849
- PMCID: PMC1324791
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0509849103
Autoantibodies to myelin basic protein catalyze site-specific degradation of their antigen
Abstract
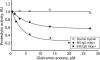
Autoantibody-mediated tissue destruction is among the main features of organ-specific autoimmunity. This report describes "an antibody enzyme" (abzyme) contribution to the site-specific degradation of a neural antigen. We detected proteolytic activity toward myelin basic protein (MBP) in the fraction of antibodies purified from the sera of humans with multiple sclerosis (MS) and mice with induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Chromatography and zymography data demonstrated that the proteolytic activity of this preparation was exclusively associated with the antibodies. No activity was found in the IgG fraction of healthy donors. The human and murine abzymes efficiently cleaved MBP but not other protein substrates tested. The sites of MBP cleavage determined by mass spectrometry were localized within immunodominant regions of MBP. The abzymes could also cleave recombinant substrates containing encephalytogenic MBP(85-101) peptide. An established MS therapeutic Copaxone appeared to be a specific abzyme inhibitor. Thus, the discovered epitope-specific antibody-mediated degradation of MBP suggests a mechanistic explanation of the slow development of neurodegeneration associated with MS.
Figures


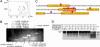
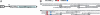
Similar articles
-
Multiple sites of the cleavage of 17- and 19-mer encephalytogenic oligopeptides corresponding to human myelin basic protein (MBP) by specific anti-MBP antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Peptides. 2012 Sep;37(1):69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Peptides. 2012. PMID: 22781164
-
Recognition and degradation of myelin basic protein peptides by serum autoantibodies: novel biomarker for multiple sclerosis.J Immunol. 2008 Jan 15;180(2):1258-67. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.2.1258. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18178866
-
Multiple Sclerosis: Enzymatic Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H1 Histone by IgGs against H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4 Histones, and Myelin Basic Protein.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 2;11(8):1140. doi: 10.3390/biom11081140. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439806 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic and pathogenetic implications of the site specificity of antibody proteases in multiple sclerosis].Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2010;(4):8-15. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2010. PMID: 20540348 Review. Russian.
-
[Mechanisms involved in the regulation of immune response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006;60:571-83. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006. PMID: 17115007 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Catalytic Antibodies May Contribute to Demyelination in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.Biochemistry. 2024 Jan 2;63(1):9-18. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00433. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38011893 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Antibodies with Amylase Activity from Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis.PLoS One. 2016 May 19;11(5):e0154688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154688. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27196086 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantigen microarrays reveal myelin basic protein autoantibodies in morphea.J Transl Med. 2022 Jan 24;20(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03246-5. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35073943 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Antibodies Produced in Vaccinated Patients and COVID-19 Convalescents Hydrolyze Recombinant RBD and Nucleocapsid (N) Proteins.Biomedicines. 2024 May 2;12(5):1007. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051007. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38790969 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-Infected Patients: Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H3 and H4 Histones and Myelin Basic Protein with Antibodies against These Three Proteins.Molecules. 2021 Jan 9;26(2):316. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020316. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33435385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwartz, R. S. (1993) in Fundamental Immunology, ed. Paul, W. E. (Raven, New York), pp. 1033-1097.
-
- Hofstetter, H. H., Sewell, D. L., Liu, F., Sandor, M., Forsthuber, T., Lehmann, P. V. & Fabry, Z. (2003) J. Neuroimmunol. 134, 25-34. - PubMed
-
- Hohlfeld, R. & Wekerle, H. (2001) Curr. Opin. Neurol. 14, 299-304. - PubMed
-
- Archelos, J. J., Storch, M. K. & Hartung, H. P. (2000) Ann. Neurol. 47, 694-706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

