Determination of beta-carotene in supplements and raw materials by reversed-phase high pressure liquid chromatography: collaborative study
- PMID: 16385976
- PMCID: PMC2657295
Determination of beta-carotene in supplements and raw materials by reversed-phase high pressure liquid chromatography: collaborative study
Abstract
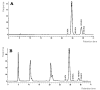
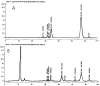
Twelve laboratories representing 4 countries participated in an interlaboratory study conducted to determine all-trans-veta-carotene and total beta-carotene in dietary supplements and raw materials. Thirteen samples were sent as blind duplicates to the collaborators. Results obtained from 11 laboratories are reported. For products composed as softgels and tablets that were analyzed for total beta-carotene, the reproducibility relative standard deviation (RSDR) ranged from 3.35 to 23.09% and the HorRat values ranged from 1.06 to 3.72. For these products analyzed for trans beta-carotene, the reproducibility relative standard deviation (RSDR) ranged from 4.28 to 22.76% and the HorRat values ranged from 0.92 to 3.37. The RSDr and HorRat values in the analysis of a beadlet raw material were substantial and it is believed that the variability within the material itself introduced significant variation in subsampling. The method uses high pressure liquid chromatography (LC) in the reversed-phase mode with visible light absorbance for detection and quantitation. If high levels of alpha-carotenes are present, a second LC system is used for additional separation and quantitation of the carotene species. It is recommended that the method be adopted as an AOAC Official Method.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of lycopene in dietary supplements and raw materials by high-performance liquid chromatography: collaborative study.J AOAC Int. 2010 Mar-Apr;93(2):499-509. J AOAC Int. 2010. PMID: 20480896
-
Method for the determination of beta-carotene in supplements and raw materials by reversed-phase liquid chromatography: single laboratory validation.J AOAC Int. 2004 Sep-Oct;87(5):1070-82. J AOAC Int. 2004. PMID: 15493663 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of coenzyme Q10 content in raw materials and dietary supplements by high-performance liquid chromatography-UV: collaborative study.J AOAC Int. 2008 Jul-Aug;91(4):702-8. J AOAC Int. 2008. PMID: 18727527 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of glucosamine in raw materials and dietary supplements containing glucosamine sulfate and/or glucosamine hydrochloride by high-performance liquid chromatography with FMOC-Su derivatization: collaborative study.J AOAC Int. 2005 Jul-Aug;88(4):1048-58. J AOAC Int. 2005. PMID: 16152919 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the Determination of the Antioxidant Activity of Foods, Food Ingredients, and Dietary Supplements by Thin Layer Chromatography-Direct Bioautography, Spectrometry, and the Dot-Blot Procedure.J AOAC Int. 2018 Sep 1;101(5):1285-1294. doi: 10.5740/jaoacint.18-0116. Epub 2018 May 31. J AOAC Int. 2018. PMID: 29852892 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary supplement ingredient database (DSID): Preliminary USDA studies on the composition of adult multivitamin/mineral supplements.J Food Compost Anal. 2008 Feb;21(Suppl 1):S69-S77. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2007.07.009. J Food Compost Anal. 2008. PMID: 24307755 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical ingredient content and variability of adult multivitamin/mineral products: national estimates for the Dietary Supplement Ingredient Database.Am J Clin Nutr. 2017 Feb;105(2):526-539. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.134544. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27974309 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Method Selection in Determining Product Integrity for Nutrition Research.Adv Nutr. 2016 Mar 15;7(2):390-8. doi: 10.3945/an.115.010611. Print 2016 Mar. Adv Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26980823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges to Quantify Total Vitamin Activity: How to Combine the Contribution of Diverse Vitamers?Curr Dev Nutr. 2019 Jul 25;3(10):nzz086. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzz086. eCollection 2019 Oct. Curr Dev Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31598575 Free PMC article. Review.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical