Contributions of Trf4p- and Trf5p-dependent polyadenylation to the processing and degradative functions of the yeast nuclear exosome
- PMID: 16373491
- PMCID: PMC1370882
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2207206
Contributions of Trf4p- and Trf5p-dependent polyadenylation to the processing and degradative functions of the yeast nuclear exosome
Abstract
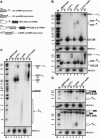
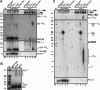
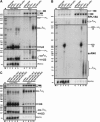
The nuclear exosome is involved in a large number of RNA processing and surveillance pathways. RNase III cleavage intermediates destined to be 3'-processed or degraded can be detected when the Rrp6p subunit of the nuclear exosome is absent. Here we show that these processing and degradation intermediates are polyadenylated, and that their polyadenylation is dependent on the activity of Trf4p and Trf5p, two variant poly(A) polymerases. Polyadenylation of cleavage intermediates was inhibited when Trf4p was absent, and reduced to various extents in the absence of Trf5p, suggesting that these two poly(A) polymerases play functionally distinct roles in the polyadenylation of these RNA species. Finally, in the absence of Trf4p, we observed 3'-extended forms of the U4 snRNA that are similar to those observed in the absence of Rrp6p. These results suggest that polyadenylation of RNA processing intermediates plays a functional role in RNA processing pathways and is not limited to RNA surveillance functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear RNA surveillance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Trf4p-dependent polyadenylation of nascent hypomethylated tRNA and an aberrant form of 5S rRNA.RNA. 2006 Mar;12(3):508-21. doi: 10.1261/rna.2305406. Epub 2006 Jan 23. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16431988 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast Trf5p is a nuclear poly(A) polymerase.EMBO Rep. 2006 Feb;7(2):205-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400612. EMBO Rep. 2006. PMID: 16374505 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting mechanisms of nuclear mRNA surveillance in THO/sub2 complex mutants.EMBO J. 2007 May 2;26(9):2317-26. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601669. Epub 2007 Apr 5. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17410208 Free PMC article.
-
The 3' end formation in small RNAs.Gene Expr. 2002;10(1-2):59-78. Gene Expr. 2002. PMID: 11868988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New ways to meet your (3') end oligouridylation as a step on the path to destruction.Genes Dev. 2008 Jan 1;22(1):1-7. doi: 10.1101/gad.1634508. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18172159 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Expression of Subtelomeric lncRNAs Links Telomeres Dynamics to RNA Decay in S. cerevisiae.Noncoding RNA. 2015 Jul 3;1(2):94-126. doi: 10.3390/ncrna1020094. Noncoding RNA. 2015. PMID: 29861418 Free PMC article.
-
Cotranscriptional recruitment of yeast TRAMP complex to intronic sequences promotes optimal pre-mRNA splicing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(1):643-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt888. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24097436 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(A) polymerase (PAP) diversity in gene expression--star-PAP vs canonical PAP.FEBS Lett. 2014 Jun 27;588(14):2185-97. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.05.029. Epub 2014 May 27. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24873880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diurnal Oscillations in Liver Mass and Cell Size Accompany Ribosome Assembly Cycles.Cell. 2017 May 4;169(4):651-663.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.015. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28475894 Free PMC article.
-
Two conserved regulatory cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerases, GLD-4 and GLD-2, regulate meiotic progression in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2009 Apr 1;23(7):824-36. doi: 10.1101/gad.494009. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19339688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abou Elela, S., Igel, H., and Ares Jr., M. 1996. RNase III cleaves eukaryotic preribosomal RNA at a U3 snoRNP-dependent site. Cell 85: 115–124. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet-Antonelli, C., Presutti, C., and Tollervey, D. 2000. Identification of a regulated pathway for nuclear pre-mRNA turnover. Cell 102: 765–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
