Activation of NK cells by an endocytosed receptor for soluble HLA-G
- PMID: 16366734
- PMCID: PMC1318474
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040009
Activation of NK cells by an endocytosed receptor for soluble HLA-G
Abstract
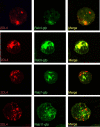
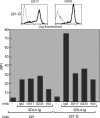
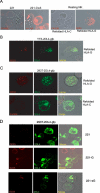
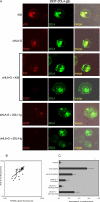
Signaling from endosomes is emerging as a mechanism by which selected receptors provide sustained signals distinct from those generated at the plasma membrane. The activity of natural killer (NK) cells, which are important effectors of innate immunity and regulators of adaptive immunity, is controlled primarily by receptors that are at the cell surface. Here we show that cytokine secretion by resting human NK cells is induced by soluble, but not solid-phase, antibodies to the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) 2DL4, a receptor for human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-G. KIR2DL4 was constitutively internalized into Rab5-positive compartments via a dynamin-dependent process. Soluble HLA-G was endocytosed into KIR2DL4-containing compartments in NK cells and in 293T cells transfected with KIR2DL4. Chemokine secretion induced by KIR2DL4 transfection into 293T cells occurred only with recombinant forms of KIR2DL4 that trafficked to endosomes. The profile of genes up-regulated by KIR2DL4 engagement on resting NK cells revealed a proinflammatory/proangiogenic response. Soluble HLA-G induced secretion of a similar set of cytokines and chemokines. This unique stimulation of resting NK cells by soluble HLA-G, which is endocytosed by KIR2DL4, implies that NK cells may provide useful functions at sites of HLA-G expression, such as promotion of vascularization in maternal decidua during early pregnancy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-G-specific receptor expressed on all natural killer cells.J Exp Med. 1999 Apr 5;189(7):1093-100. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.7.1093. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10190900 Free PMC article.
-
Possible roles of KIR2DL4 expression on uNK cells in human pregnancy.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2007 Apr;57(4):233-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2007.00469.x. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17362384
-
Residues Met76 and Gln79 in HLA-G alpha1 domain involve in KIR2DL4 recognition.Cell Res. 2005 Mar;15(3):176-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290283. Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15780179
-
Endosomal signaling and a novel pathway defined by the natural killer receptor KIR2DL4 (CD158d).Traffic. 2010 Nov;11(11):1381-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01112.x. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20854369 Review.
-
Roles of HLA-G/KIR2DL4 in Breast Cancer Immune Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 3;13:791975. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.791975. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35185887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human leucocyte antigen-G (HLA-G) and its murine functional homolog Qa2 in the Trypanosoma cruzi Infection.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:595829. doi: 10.1155/2015/595829. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25688175 Free PMC article.
-
No time to die: Epigenetic regulation of natural killer cell survival.Immunol Rev. 2024 May;323(1):61-79. doi: 10.1111/imr.13314. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38426615 Review.
-
Organ-specific phenotypic and functional features of NK cells in humans.Immunol Res. 2014 Jan;58(1):125-31. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8477-9. Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24366663 Review.
-
Effect of interleukins (IL-2, IL-15, IL-18) on receptors activation and cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells in breast cancer cell.Afr Health Sci. 2020 Jun;20(2):822-832. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v20i2.36. Afr Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 33163049 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum soluble human leukocyte antigen-G levels with chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Clin Exp Med. 2014 Feb;14(1):35-43. doi: 10.1007/s10238-012-0214-5. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 23007926
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

