The protein phosphatase AtPP2CA negatively regulates abscisic acid signal transduction in Arabidopsis, and effects of abh1 on AtPP2CA mRNA
- PMID: 16361522
- PMCID: PMC1326037
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.105.070318
The protein phosphatase AtPP2CA negatively regulates abscisic acid signal transduction in Arabidopsis, and effects of abh1 on AtPP2CA mRNA
Abstract
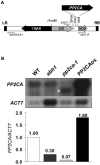
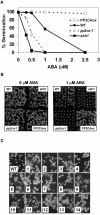
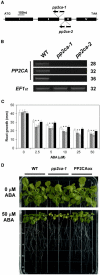
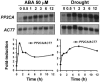
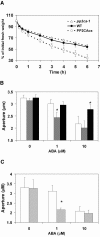
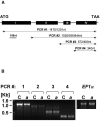
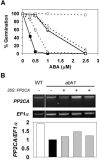
To identify new loci in abscisic acid (ABA) signaling, we screened a library of 35ScDNA Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana)-expressing lines for ABA-insensitive mutants in seed germination assays. One of the identified mutants germinated on 2.5 microm ABA, a concentration that completely inhibits wild-type seed germination. Backcrosses and F2 analyses indicated that the mutant exhibits a dominant phenotype and that the ABA insensitivity was linked to a single T-DNA insertion containing a 35ScDNA fusion. The inserted cDNA corresponds to a full-length cDNA of the AtPP2CA gene, encoding a protein phosphatase type 2C (PP2C). Northern-blot analyses demonstrated that the AtPP2CA transcript is indeed overexpressed in the mutant (named PP2CAox). Two independent homozygous T-DNA insertion lines, pp2ca-1 and pp2ca-2, were recovered from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center and shown to lack full-length AtPP2CA expression. A detailed characterization of PP2CAox and the T-DNA disruption mutants demonstrated that, whereas ectopic expression of a 35SAtPP2CA fusion caused ABA insensitivity in seed germination and ABA-induced stomatal closure responses, disruption mutants displayed the opposite phenotype, namely, strong ABA hypersensitivity. Thus our data demonstrate that the PP2CA protein phosphatase is a strong negative regulator of ABA signal transduction. Furthermore, it has been previously shown that the AtPP2CA transcript is down-regulated in the ABA-hypersensitive nuclear mRNA cap-binding protein mutant abh1. We show here that down-regulation of AtPP2CA in abh1 is not due to impaired RNA splicing of AtPP2CA pre-mRNA. Moreover, expression of a 35SAtPP2CA cDNA fusion in abh1 partially suppresses abh1 hypersensitivity, and the data further suggest that additional mechanisms contribute to ABA hypersensitivity of abh1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ABA-hypersensitive germination3 encodes a protein phosphatase 2C (AtPP2CA) that strongly regulates abscisic acid signaling during germination among Arabidopsis protein phosphatase 2Cs.Plant Physiol. 2006 Jan;140(1):115-26. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.070128. Epub 2005 Dec 9. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16339800 Free PMC article.
-
Localization, ion channel regulation, and genetic interactions during abscisic acid signaling of the nuclear mRNA cap-binding protein, ABH1.Plant Physiol. 2002 Nov;130(3):1276-87. doi: 10.1104/pp.009480. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12427994 Free PMC article.
-
ABA-Hypersensitive Germination1 encodes a protein phosphatase 2C, an essential component of abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis seed.Plant J. 2007 Jun;50(6):935-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03107.x. Epub 2007 Apr 25. Plant J. 2007. PMID: 17461784
-
mRNA cap binding proteins: effects on abscisic acid signal transduction, mRNA processing, and microarray analyses.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;326:139-50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-76776-3_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18630751 Review.
-
Protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C) function in higher plants.Plant Mol Biol. 1998 Dec;38(6):919-27. doi: 10.1023/a:1006054607850. Plant Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9869399 Review.
Cited by
-
Leaf temperature responses to ABA and dead bacteria in wheat and Arabidopsis.Plant Signal Behav. 2021 May 4;16(5):1899471. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2021.1899471. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Plant Signal Behav. 2021. PMID: 33704000 Free PMC article.
-
Unique drought resistance functions of the highly ABA-induced clade A protein phosphatase 2Cs.Plant Physiol. 2012 Sep;160(1):379-95. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.202408. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22829320 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of abscisic acid sensitivity and reduction of water consumption in Arabidopsis by combined inactivation of the protein phosphatases type 2C ABI1 and HAB1.Plant Physiol. 2006 Aug;141(4):1389-99. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.081018. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16798945 Free PMC article.
-
Early abscisic acid signal transduction mechanisms: newly discovered components and newly emerging questions.Genes Dev. 2010 Aug 15;24(16):1695-708. doi: 10.1101/gad.1953910. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20713515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of an important site for function of the type 2C protein phosphatase ABI2 in abscisic acid signalling in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2011 Nov;62(15):5713-25. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err274. Epub 2011 Sep 1. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 21885535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana Nature 408: 796–815 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

