Two classes of endogenous small RNAs in Tetrahymena thermophila
- PMID: 16357212
- PMCID: PMC1356098
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1377006
Two classes of endogenous small RNAs in Tetrahymena thermophila
Abstract
Endogenous small RNAs function in RNA interference (RNAi) pathways to guide RNA cleavage, translational repression, or methylation of DNA or chromatin. In Tetrahymena thermophila, developmentally regulated DNA elimination is governed by an RNAi mechanism involving approximately 27-30-nucleotide (nt) RNAs. Here we characterize the sequence features of the approximately 27-30-nt RNAs and a approximately 23-24-nt RNA class representing a second RNAi pathway. The approximately 23-24-nt RNAs accumulate strain-specifically manner and map to the genome in clusters that are antisense to predicted genes. These findings reveal the existence of distinct endogenous RNAi pathways in the unicellular T. thermophila, a complexity previously demonstrated only in multicellular organisms.
Figures

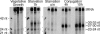
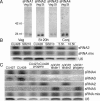
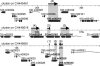
Similar articles
-
Small RNAs in genome rearrangement in Tetrahymena.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004 Apr;14(2):181-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2004.01.004. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004. PMID: 15196465 Review.
-
2'-O-methylation stabilizes Piwi-associated small RNAs and ensures DNA elimination in Tetrahymena.RNA. 2009 Apr;15(4):675-85. doi: 10.1261/rna.1455509. Epub 2009 Feb 24. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19240163 Free PMC article.
-
Germ line transcripts are processed by a Dicer-like protein that is essential for developmentally programmed genome rearrangements of Tetrahymena thermophila.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;25(20):9151-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.20.9151-9164.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16199890 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental identification and analysis of macronuclear non-coding RNAs from the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(3):1267-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr792. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21967850 Free PMC article.
-
Those interfering little RNAs! Silencing and eliminating chromatin.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004 Apr;14(2):174-80. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2004.02.006. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004. PMID: 15196464 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational analysis of mouse piRNA sequence and biogenesis.PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Nov;3(11):e222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030222. Epub 2007 Sep 28. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17997596 Free PMC article.
-
Treasure hunt in an amoeba: non-coding RNAs in Dictyostelium discoideum.Curr Genet. 2007 Mar;51(3):141-59. doi: 10.1007/s00294-006-0112-z. Curr Genet. 2007. PMID: 17171561 Review.
-
Regulation of small RNA stability: methylation and beyond.Cell Res. 2012 Apr;22(4):624-36. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.36. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22410795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of gene silencing by hairpin RNA expression in Tetrahymena thermophila reveals a second small RNA pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(23):8731-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01430-06. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17000759 Free PMC article.
-
A growth-essential Tetrahymena Piwi protein carries tRNA fragment cargo.Genes Dev. 2010 Dec 15;24(24):2742-7. doi: 10.1101/gad.1996210. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 21106669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V., Lee, R.C., Lavanway, A., Williams, P.T., and Jewell, D. 2003. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 13: 807–818. - PubMed
-
- Aravin A.A., Lagos-Quintana, M., Yalcin, A., Zavolan, M., Marks, D., Snyder, B., Gaasterland, T., Meyer, J., and Tuschl, T. 2003. The small RNA profile during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev. Cell. 5: 337–350. - PubMed
-
- Bartel B. 2005. MicroRNAs directing siRNA biogenesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12: 569–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
