Osteoclasts; culprits in inflammatory osteolysis
- PMID: 16356195
- PMCID: PMC1526550
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1857
Osteoclasts; culprits in inflammatory osteolysis
Abstract
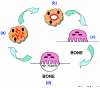
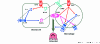
Periarticular osteolysis, a crippling complication of rheumatoid arthritis, is the product of enhanced osteoclast recruitment and activation. The osteoclast, which is a member of the monocyte/macrophage family, is the exclusive bone resorptive cell, and its differentiation and activation are under the aegis of a variety of cytokines. Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) and macrophage colony-stimulating factor are the essential osteoclastogenic cytokines and are increased in inflammatory joint disease. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, which perpetrates arthritic bone loss, exerts its osteoclastogenic effect in the context of RANKL with which it synergizes. Achieving an understanding of the mechanisms by which the three cytokines affect the osteoclast has resulted in a number of active and candidate therapeutic targets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bone and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis: what is really happening?J Rheumatol Suppl. 2002 Sep;65:44-8. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12236623 Review.
-
Sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced osteolysis through the suppression of NF-kappaB activity.J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Nov;19(11):1905-16. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040919. Epub 2004 Sep 27. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 15476591
-
CCR1 chemokines promote the chemotactic recruitment, RANKL development, and motility of osteoclasts and are induced by inflammatory cytokines in osteoblasts.J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Dec;19(12):2065-77. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040910. Epub 2004 Sep 20. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 15537451
-
Synovial fluid macrophages are capable of osteoclast formation and resorption.J Pathol. 2006 Jan;208(1):35-43. doi: 10.1002/path.1891. J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16278818
-
Bone loss in inflammatory arthritis: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches with bisphosphonates.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2005 Dec;19(6):1065-79. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2005.06.008. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 16301197 Review.
Cited by
-
Rac1 Inhibition Via Srgap2 Restrains Inflammatory Osteoclastogenesis and Limits the Clastokine, SLIT3.J Bone Miner Res. 2020 Apr;35(4):789-800. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3945. Epub 2020 Jan 9. J Bone Miner Res. 2020. PMID: 31880824 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of alcohol use with radiographic disease progression in African Americans with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2013 Sep;40(9):1498-504. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.121325. Epub 2013 Jun 15. J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23772080 Free PMC article.
-
Selective targeting of RANK signaling pathways as new therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010 Sep;14(9):923-34. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2010.511179. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010. PMID: 20678025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling has therapeutic implications for inflammatory osteolysis.Bone. 2010 Mar;46(3):695-702. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.10.032. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Bone. 2010. PMID: 19895919 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclast precursor interaction with bone matrix induces osteoclast formation directly by an interleukin-1-mediated autocrine mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 11;283(15):9917-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706415200. Epub 2008 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18250170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldring SR, Clark CR, Wright TM. The problem in total joint arthroplasty: aseptic loosening. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery – American Volume. 1993;75:799–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

