Rhp51-dependent recombination intermediates that do not generate checkpoint signal are accumulated in Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad60 and smc5/6 mutants after release from replication arrest
- PMID: 16354704
- PMCID: PMC1317627
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.343-353.2006
Rhp51-dependent recombination intermediates that do not generate checkpoint signal are accumulated in Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad60 and smc5/6 mutants after release from replication arrest
Abstract
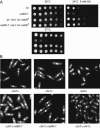
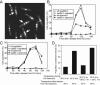
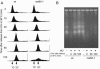
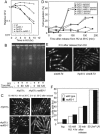
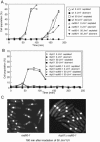
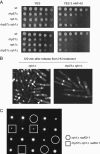
The Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad60 gene is essential for cell growth and is involved in repairing DNA double-strand breaks. Rad60 physically interacts with and is functionally related to the structural maintenance of chromosomes 5 and 6 (SMC5/6) protein complex. In this study, we investigated the role of Rad60 in the recovery from the arrest of DNA replication induced by hydroxyurea (HU). rad60-1 mutant cells arrested mitosis normally when treated with HU. Significantly, Rad60 function is not required during HU arrest but is required on release. However, the mutant cells underwent aberrant mitosis accompanied by irregular segregation of chromosomes, and DNA replication was not completed, as revealed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. The deletion of rhp51 suppressed the aberrant mitosis of rad60-1 cells and caused mitotic arrest. These results suggest that Rhp51 and Rad60 are required for the restoration of a stalled or collapsed replication fork after release from the arrest of DNA replication by HU. The rad60-1 mutant was proficient in Rhp51 focus formation after release from the HU-induced arrest of DNA replication or DNA-damaging treatment. Furthermore, the lethality of a rad60-1 rqh1Delta double mutant was suppressed by the deletion of rhp51 or rhp57. These results suggest that Rad60 is required for recombination repair at a step downstream of Rhp51. We propose that Rhp51-dependent DNA structures that cannot activate the mitotic checkpoints accumulate in rad60-1 cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Cds1Chk2 regulates homologous recombination at stalled replication forks through the phosphorylation of recombination protein Rad60.J Cell Sci. 2009 Oct 15;122(Pt 20):3638-43. doi: 10.1242/jcs.046508. Epub 2009 Sep 15. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19755492 Free PMC article.
-
Rad62 protein functionally and physically associates with the smc5/smc6 protein complex and is required for chromosome integrity and recombination repair in fission yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(21):9401-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.21.9401-9413.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15485909 Free PMC article.
-
The Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad60 gene is essential for repairing double-strand DNA breaks spontaneously occurring during replication and induced by DNA-damaging agents.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(10):3537-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.10.3537-3548.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11971984 Free PMC article.
-
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Assays to Study Mitotic Recombination Outcomes.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 10;11(1):79. doi: 10.3390/genes11010079. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fission yeast Swi5 protein, a novel DNA recombination mediator.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Jan 1;7(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Aug 22. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 17716957 Review.
Cited by
-
The Smc5/Smc6/MAGE complex confers resistance to caffeine and genotoxic stress in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059866. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555814 Free PMC article.
-
Smc5/6 is required for repair at collapsed replication forks.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(24):9387-401. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01335-06. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17030601 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases in genome stability.EMBO J. 2007 Sep 19;26(18):4089-101. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601838. Epub 2007 Aug 30. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17762865 Free PMC article.
-
Esc2 and Sgs1 act in functionally distinct branches of the homologous recombination repair pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Mar;20(6):1683-94. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-08-0877. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19158388 Free PMC article.
-
A SUMO-like domain protein, Esc2, is required for genome integrity and sister chromatid cohesion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2008 Sep;180(1):41-50. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.086249. Epub 2008 Aug 30. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18757937 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
