Active ERK1 is dimerized in vivo: bisphosphodimers generate peak kinase activity and monophosphodimers maintain basal ERK1 activity
- PMID: 16317051
- PMCID: PMC3292877
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.02683
Active ERK1 is dimerized in vivo: bisphosphodimers generate peak kinase activity and monophosphodimers maintain basal ERK1 activity
Erratum in
- J Cell Sci. 2006 May 1;119(Pt 9):1973
Abstract
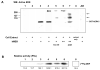
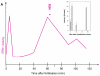
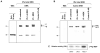
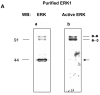
ERK1 and ERK2 are widely involved in cell signalling. Using a recombinant approach, it has been shown that exogenous ERK2 is capable of dimerization and that preventing dimerization reduces its nuclear accumulation on stimulation. Dimerization occurs on phosphorylation; the dimer partner of phosphorylated ERK2 may be either phosphorylated or unphosphorylated. It has been assumed that monophosphodimers are hemiactive. Here we show that ERK1 is capable of dimerization both in vivo and in vitro. Dimerization of human recombinant ERK1 in vitro requires both ERK1 phosphorylation and cellular cofactor(s); it leads to the formation of a high molecular weight complex that can be dissociated by treatment with beta-mercaptoethanol. We demonstrate for the first time in both sea urchin embryos and human cells that native ERK forms dimers and that high ERK kinase activity is largely associated with bisphosphodimers, not with monophosphodimers or phosphorylated monomers. The activity of the bisphosphodimer is about 20-fold higher than that of the phosphorylated monomer in vitro and the bisphosphodimer shows 5- to 7-fold higher in vivo activity than the basal activity attributable to the monophosphodimer. Thus phosphorylation of both partners in the dimer is a hallmark of ERK activation. Judgments made about ERK kinase activity associated with phosphorylated monomers are at best a proxy for ERK activity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Rho kinase-induced nuclear translocation of ERK1/ERK2 in smooth muscle cell mitogenesis caused by serotonin.Circ Res. 2004 Sep 17;95(6):579-86. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000141428.53262.a4. Epub 2004 Aug 5. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15297378
-
Crystal structure of human mono-phosphorylated ERK1 at Tyr204.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Dec 26;377(4):1123-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.10.127. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18983981
-
Phosphorylation of the MAP kinase ERK2 promotes its homodimerization and nuclear translocation.Cell. 1998 May 15;93(4):605-15. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81189-7. Cell. 1998. PMID: 9604935
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 has duality in function between neuronal and astrocyte expression following neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic cerebral injury.J Physiol. 2018 Dec;596(23):6043-6062. doi: 10.1113/JP275649. Epub 2018 Jul 11. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29873394 Free PMC article.
-
Dimerization in MAP-kinase signaling.Trends Biochem Sci. 2000 Jan;25(1):7-9. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01508-x. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000. PMID: 10637602 Review.
Cited by
-
TLR7 Agonists Modulate the Activation of Human Conjunctival Epithelial Cells Induced by IL-1β via the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2023 Aug;46(4):1430-1444. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01818-1. Epub 2023 May 8. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 37154978
-
RAS Dimers: The Novice Couple at the RAS-ERK Pathway Ball.Genes (Basel). 2021 Sep 30;12(10):1556. doi: 10.3390/genes12101556. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MEK/ERK Network as a Therapeutic Target in Human Cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Mar;19(3):361-374. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0687. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33139506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus Hsp90 interacts with the main components of the cell wall integrity pathway and cooperates in heat shock and cell wall stress adaptation.Cell Microbiol. 2021 Feb;23(2):e13273. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13273. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Cell Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33010083 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Kinase Activity: ERK5 Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling as a Novel Target for Anticancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 31;21(3):938. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030938. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32023850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrieu A, Doree M, Fisher D. The interplay between cyclin-B-Cdc2 kinase (MPF) and MAP kinase during maturation of oocytes. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:257–67. - PubMed
-
- Canagarajah B, Khokhlatchev AV, Cobb MH, Goldsmith E. Activation mechanism of the MAP kinase ERK2 by dual phosphorylation. Cell. 1997;90:859–869. - PubMed
-
- Choi KY, Satterberg B, Lyons DM, Elion EA. Ste5 tethers multiple protein kinases in the MAP kinase cascade required for mating in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1994;78:499–512. - PubMed
-
- Cobb MH, Goldsmith E. Dimerization in MAP-kinase signaling. TIBS. 2000;25:7–9. - PubMed
-
- English J, Pearson G, Wilsbacher J, Swantek J, Karandikar M, Xu S, Cobb MH. New insights into the control of MAP kinase pathways. Exp Cell Res. 1999;253:255–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

