Small interfering RNAs containing full 2'-O-methylribonucleotide-modified sense strands display Argonaute2/eIF2C2-dependent activity
- PMID: 16301602
- PMCID: PMC1370895
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2150806
Small interfering RNAs containing full 2'-O-methylribonucleotide-modified sense strands display Argonaute2/eIF2C2-dependent activity
Abstract
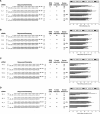
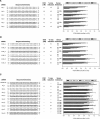
RNA interference (RNAi) is a process by which short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) direct the degradation of complementary single-strand RNAs. In this study, we investigated the effects of full-strand phosphorothioate (PS) backbone and 2'-O-methyl (2'-OMe) sugar modifications on RNAi-mediated silencing. In contrast to previous reports, we have identified active siRNA duplexes containing full 2'-OMe-modified sense strands that display comparable activity to the unmodified analog of similar sequence. The structure of these modified siRNAs is the predominant determinant of their activity, with sequence and backbone composition being secondary. We further show, by using biotin-tagged siRNAs and affinity-tagged hAgo2/eIF2C2, that activity of siRNA duplexes containing full 2'-OMe substitutions in the sense strand is mediated by the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and that strand-specific loading (or binding) to hAgo2 may be modulated through selective incorporation of these modifications.
Figures
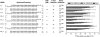
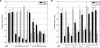
Similar articles
-
RNA interference tolerates 2'-fluoro modifications at the Argonaute2 cleavage site.Chem Biodivers. 2007 May;4(5):858-73. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200790073. Chem Biodivers. 2007. PMID: 17511001
-
The 5' binding MID domain of human Argonaute2 tolerates chemically modified nucleotide analogues.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013 Feb;23(1):81-7. doi: 10.1089/nat.2012.0393. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013. PMID: 23289589
-
Sequence, chemical, and structural variation of small interfering RNAs and short hairpin RNAs and the effect on mammalian gene silencing.Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2003 Apr;13(2):83-105. doi: 10.1089/108729003321629638. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2003. PMID: 12804036
-
The Argonautes.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:67-72. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.048. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381282 Review.
-
Technology of RNA Interference in Advanced Medicine.Microrna. 2018;7(2):74-84. doi: 10.2174/2211536607666180129153307. Microrna. 2018. PMID: 29380708 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Therapeutic-Grade Small Interfering RNAs by Chemical Engineering.Front Genet. 2012 Aug 20;3:154. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00154. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 22934103 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects between analogs of DNA and RNA improve the potency of siRNA-mediated gene silencing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul;38(13):4547-57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq181. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20413581 Free PMC article.
-
Improving gene silencing of siRNAs via tricyclo-DNA modification.Artif DNA PNA XNA. 2010 Jul;1(1):9-16. doi: 10.4161/adna.1.1.11385. Artif DNA PNA XNA. 2010. PMID: 21687522 Free PMC article.
-
Ratiometric, pH-Sensitive Probe for Monitoring siRNA Delivery.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 May 3;145(17):9417-9422. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c01032. Epub 2023 Apr 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37075200 Free PMC article.
-
Nearest neighbor parameters for Watson-Crick complementary heteroduplexes formed between 2'-O-methyl RNA and RNA oligonucleotides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 26;34(13):3609-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl232. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16870722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allerson, C.R., Sioufi, N., Jarres, R., Prakash, T.P., Naik, N., Berdeja, A., Wanders, L., Griffey, R.H., Swayze, E.E., and Bhat, B. 2005. Fully 2′-modified oligonucleotide duplexes with improved in vitro potency and stability compared to unmodified small interfering RNA. J. Med. Chem. 48: 901–904. - PubMed
-
- Altmann, K.H., Fabbro, D., Dean, N.M., Geiger, T., Monia, B.P., Muller, M., and Nicklin, P. 1996. Second-generation antisense oligonucleotides: Structure–activity relationships and the design of improved signal-transduction inhibitors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 24: 630–637. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, C.F. and Cowsert, L.M. 1999. Antisense oligonucleotides as a tool for gene functionalization and target validation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1489: 19–30. - PubMed
-
- Braasch, D.A. and Corey, D.R. 2002. Novel antisense and peptide nucleic acid strategies for controlling gene expression. Biochemistry 41: 4503–4510. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
