RBP-Jkappa/SHARP recruits CtIP/CtBP corepressors to silence Notch target genes
- PMID: 16287852
- PMCID: PMC1291242
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10379-10390.2005
RBP-Jkappa/SHARP recruits CtIP/CtBP corepressors to silence Notch target genes
Abstract
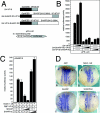
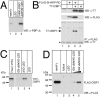
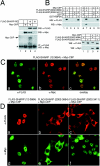
Notch is a transmembrane receptor that determines cell fates and pattern formation in all animal species. After ligand binding, proteolytic cleavage steps occur and the intracellular part of Notch translocates to the nucleus, where it targets the DNA-binding protein RBP-Jkappa/CBF1. In the absence of Notch, RBP-Jkappa represses Notch target genes through the recruitment of a corepressor complex. We and others have identified SHARP as a component of this complex. Here, we functionally demonstrate that the SHARP repression domain is necessary and sufficient to repress transcription and that the absence of this domain causes a dominant negative Notch-like phenotype. We identify the CtIP and CtBP corepressors as novel components of the human RBP-Jkappa/SHARP-corepressor complex and show that CtIP binds directly to the SHARP repression domain. Functionally, CtIP and CtBP augment SHARP-mediated repression. Transcriptional repression of the Notch target gene Hey1 is abolished in CtBP-deficient cells or after the functional knockout of CtBP. Furthermore, the endogenous Hey1 promoter is derepressed in CtBP-deficient cells. We propose that a corepressor complex containing CtIP/CtBP facilitates RBP-Jkappa/SHARP-mediated repression of Notch target genes.
Figures

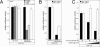
Similar articles
-
ETO, but not leukemogenic fusion protein AML1/ETO, augments RBP-Jkappa/SHARP-mediated repression of notch target genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;28(10):3502-12. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01966-07. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18332109 Free PMC article.
-
SHARP is a novel component of the Notch/RBP-Jkappa signalling pathway.EMBO J. 2002 Oct 15;21(20):5417-26. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf549. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12374742 Free PMC article.
-
Hairless-mediated repression of notch target genes requires the combined activity of Groucho and CtBP corepressors.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(23):10433-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10433-10441.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16287856 Free PMC article.
-
CSL-Associated Corepressor and Coactivator Complexes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1066:279-295. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-89512-3_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30030832 Review.
-
HES and HERP families: multiple effectors of the Notch signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Mar;194(3):237-55. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10208. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12548545 Review.
Cited by
-
Notch signaling pathway and human placenta.Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(6):447-52. doi: 10.7150/ijms.4593. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Int J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22859905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch Signaling in Neuroendocrine Tumors.Front Oncol. 2016 Apr 14;6:94. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00094. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27148486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone demethylase KDM5A is an integral part of the core Notch-RBP-J repressor complex.Genes Dev. 2010 Mar 15;24(6):590-601. doi: 10.1101/gad.563210. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20231316 Free PMC article.
-
The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism.Cell. 2009 Apr 17;137(2):216-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.045. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19379690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JmjC Domain-containing Protein 6 (Jmjd6) Derepresses the Transcriptional Repressor Transcription Factor 7-like 1 (Tcf7l1) and Is Required for Body Axis Patterning during Xenopus Embryogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 14;290(33):20273-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.646554. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26157142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinnadurai, G. 2002. CtBP, an unconventional transcriptional corepressor in development and oncogenesis. Mol. Cell 9:213-224. - PubMed
-
- De Strooper, B., W. Annaert, P. Cupers, P. Saftig, K. Craessaerts, J. S. Mumm, E. H. Schroeter, V. Schrijvers, M. S. Wolfe, W. J. Ray, A. Goate, and R. Kopan. 1999. A presenilin-1-dependent gamma-secretase-like protease mediates release of Notch intracellular domain. Nature 398:518-522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
