The role of Snapin in neurosecretion: snapin knock-out mice exhibit impaired calcium-dependent exocytosis of large dense-core vesicles in chromaffin cells
- PMID: 16280592
- PMCID: PMC1803083
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3275-05.2005
The role of Snapin in neurosecretion: snapin knock-out mice exhibit impaired calcium-dependent exocytosis of large dense-core vesicles in chromaffin cells
Abstract
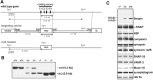
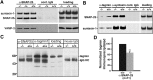
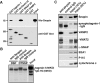
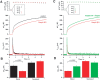
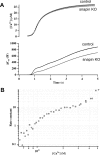
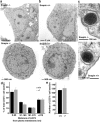
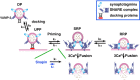
Identification of the molecules that regulate the priming of synaptic vesicles for fusion and the structural coupling of the calcium sensor with the soluble N-ethyl maleimide sensitive factor adaptor protein receptor (SNARE)-based fusion machinery is critical for understanding the mechanisms underlying calcium-dependent neurosecretion. Snapin binds to synaptosomal-associated protein 25 kDa (SNAP-25) and enhances the association of the SNARE complex with synaptotagmin. In the present study, we abolished snapin expression in mice and functionally evaluated the role of Snapin in neuroexocytosis. We found that the association of synaptotagmin-1 with SNAP-25 in brain homogenates of snapin mutant mice is impaired. Consequently, the absence of Snapin in embryonic chromaffin cells leads to a significant reduction of calcium-dependent exocytosis resulting from a decreased number of vesicles in releasable pools. Overexpression of Snapin fully rescued this inhibitory effect in the mutant cells. Furthermore, Snapin is relatively enriched in the purified large dense-core vesicles of chromaffin cells and associated with synaptotagmin-1. Thus, our biochemical and electrophysiological studies using snapin knock-out mice demonstrate that Snapin plays a critical role in modulating neurosecretion by stabilizing the release-ready vesicles.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Snapin accelerates exocytosis at low intracellular calcium concentration in mouse chromaffin cells.Cell Calcium. 2013 Aug;54(2):105-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 30. Cell Calcium. 2013. PMID: 23726552
-
Differential control of the releasable vesicle pools by SNAP-25 splice variants and SNAP-23.Cell. 2003 Jul 11;114(1):75-86. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00477-x. Cell. 2003. PMID: 12859899
-
Ca2+-induced changes in SNAREs and synaptotagmin I correlate with triggered exocytosis from chromaffin cells: insights gleaned into the signal transduction using trypsin and botulinum toxins.J Cell Sci. 2002 Jul 1;115(Pt 13):2791-800. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.13.2791. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12077369
-
Exploring the structural dynamics of the vesicle priming machinery.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Aug 28;52(4):1715-1725. doi: 10.1042/BST20231333. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 39082978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation, stabilisation and fusion of the readily releasable pool of secretory vesicles.Pflugers Arch. 2004 Jul;448(4):347-62. doi: 10.1007/s00424-004-1247-8. Epub 2004 Mar 2. Pflugers Arch. 2004. PMID: 14997396 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of synaptic activity by snapin-mediated endolysosomal transport and sorting.EMBO J. 2015 Aug 4;34(15):2059-77. doi: 10.15252/embj.201591125. Epub 2015 Jun 24. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 26108535 Free PMC article.
-
BLOS2 negatively regulates Notch signaling during neural and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell development.Elife. 2016 Oct 10;5:e18108. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18108. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27719760 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the Swimbladder Surfactant System and Biogenesis of Lysosome-Related Organelles Is Regulated by BLOS1 in Zebrafish.Genetics. 2018 Mar;208(3):1131-1146. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300621. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29339408 Free PMC article.
-
Retrograde transport of TrkB-containing autophagosomes via the adaptor AP-2 mediates neuronal complexity and prevents neurodegeneration.Nat Commun. 2017 Apr 7;8:14819. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14819. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28387218 Free PMC article.
-
Snapin is critical for presynaptic homeostatic plasticity.J Neurosci. 2012 Jun 20;32(25):8716-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5465-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22723711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustine GJ (2001) How does calcium trigger neurotransmitter release? Curr Opin Neurobiol 11: 320-326. - PubMed
-
- Bai J, Wang CT, Richards DA, Jackson MB, Chapman ER (2004) Fusion pore dynamics are regulated by synaptotagmin*t-SNARE interactions. Neuron 41: 929-942. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MK, Calakos N, Scheller RH (1992) Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science 257: 255-259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
