Androgens regulate the permeability of the blood-testis barrier
- PMID: 16275920
- PMCID: PMC1283811
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506084102
Androgens regulate the permeability of the blood-testis barrier
Abstract
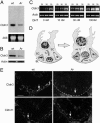
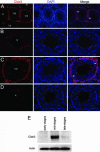
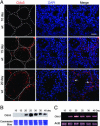
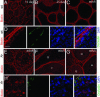
Within the mammalian testis, specialized tight junctions between somatic Sertoli cells create basal and apical polarity within the cells, restrict movement of molecules between cells, and separate the seminiferous epithelium into basal and adluminal compartments. These tight junctions form the basis of the blood-testis barrier, a structure whose function and dynamic regulation is poorly understood. In this study, we used microarray gene expression profiling to identify genes with altered transcript levels in a mouse model for conditional androgen insensitivity. We show that testosterone, acting through its receptor expressed in Sertoli cells, regulates the expression of claudin 3, which encodes a transient component of newly formed tight junctions. Sertoli cell-specific ablation of androgen receptor results in increased permeability of the blood-testis barrier to biotin, suggesting claudin 3 regulates the movement of small molecules across the Sertoli cell tight junctions. These results suggest that androgen action in Sertoli cells regulates germ cell differentiation, in part by controlling the microenvironment of the seminiferous epithelium. Our studies also indicate that hormonal strategies for male contraception may interfere with the blood-testis barrier.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disruption of Sertoli-germ cell adhesion function in the seminiferous epithelium of the rat testis can be limited to adherens junctions without affecting the blood-testis barrier integrity: an in vivo study using an androgen suppression model.J Cell Physiol. 2005 Oct;205(1):141-57. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20377. J Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15880438
-
Claudin 11 inter-sertoli tight junctions in the testis of the korean soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus maackii).Biol Reprod. 2015 Apr;92(4):96. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.114.117804. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Biol Reprod. 2015. PMID: 25761591
-
Androgen initiates Sertoli cell tight junction formation in the hypogonadal (hpg) mouse.Biol Reprod. 2012 Aug 23;87(2):38. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.094318. Print 2012 Aug. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22623623
-
The blood-testis barrier and Sertoli cell junctions: structural considerations.Microsc Res Tech. 1992 Jan 1;20(1):3-33. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070200104. Microsc Res Tech. 1992. PMID: 1611148 Review.
-
Extracellular matrix: recent advances on its role in junction dynamics in the seminiferous epithelium during spermatogenesis.Biol Reprod. 2004 Aug;71(2):375-91. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.028225. Epub 2004 Apr 28. Biol Reprod. 2004. PMID: 15115723 Review.
Cited by
-
Restoration of spermatogenesis and male fertility using an androgen receptor transgene.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 24;10(3):e0120783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120783. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25803277 Free PMC article.
-
Low Doses of Glyphosate/Roundup Alter Blood-Testis Barrier Integrity in Juvenile Rats.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 11;12:615678. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.615678. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33776912 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of paracellular permeability: factors and mechanisms.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Nov;40(11):6123-42. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2724-y. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24062072 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor pathway substrate 8 (Eps8) is a novel regulator of cell adhesion and the blood-testis barrier integrity in the seminiferous epithelium.FASEB J. 2009 Aug;23(8):2555-67. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-070573. Epub 2009 Mar 17. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19293393 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines and junction restructuring events during spermatogenesis in the testis: an emerging concept of regulation.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009 Aug;20(4):329-38. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.07.007. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009. PMID: 19651533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sharpe, R. M. (1994) in The Physiology of Reproduction, eds. Knobil, E. & Neill, J. D. (Raven, New York).
-
- McLachlan, R. I., O'Donnell, L., Meachem, S. J., Stanton, P. G., de, K., Pratis, K. & Robertson, D. M. (2002) J. Androl. 23, 149–162. - PubMed
-
- Mendis-Handagama, S. M. (1997) Histol. Histopathol. 12, 869–882. - PubMed
-
- Maekawa, M., Kamimura, K. & Nagano, T. (1996) Arch Histol. Cytol. 59, 1–13. - PubMed
-
- Griswold, M. D. (1998) Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 411–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

