Mapping determinants of human gene expression by regional and genome-wide association
- PMID: 16251966
- PMCID: PMC3005311
- DOI: 10.1038/nature04244
Mapping determinants of human gene expression by regional and genome-wide association
Abstract
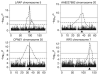
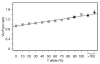
To study the genetic basis of natural variation in gene expression, we previously carried out genome-wide linkage analysis and mapped the determinants of approximately 1,000 expression phenotypes. In the present study, we carried out association analysis with dense sets of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers from the International HapMap Project. For 374 phenotypes, the association study was performed with markers only from regions with strong linkage evidence; these regions all mapped close to the expressed gene. For a subset of 27 phenotypes, analysis of genome-wide association was performed with >770,000 markers. The association analysis with markers under the linkage peaks confirmed the linkage results and narrowed the candidate regulatory regions for many phenotypes with strong linkage evidence. The genome-wide association analysis yielded highly significant results that point to the same locations as the genome scans for about 50% of the phenotypes. For one candidate determinant, we carried out functional analyses and confirmed the variation in cis-acting regulatory activity. Our findings suggest that association studies with dense SNP maps will identify susceptibility loci or other determinants for some complex traits or diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of single SNPs, haplotypes, and whole-genome LD maps on accuracy of association mapping.Genet Epidemiol. 2007 Apr;31(3):179-88. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20199. Genet Epidemiol. 2007. PMID: 17285621
-
Genetic analysis of genome-wide variation in human gene expression.Nature. 2004 Aug 12;430(7001):743-7. doi: 10.1038/nature02797. Epub 2004 Jul 21. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15269782 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association study identifies KIAA0350 as a type 1 diabetes gene.Nature. 2007 Aug 2;448(7153):591-4. doi: 10.1038/nature06010. Epub 2007 Jul 15. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17632545
-
[Current studies on susceptibility genes in rheumatoid arthritis].Nihon Rinsho. 2005 Jan;63 Suppl 1:111-6. Nihon Rinsho. 2005. PMID: 15799328 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
[Genome-wide SNP association study to identify genes related to myocardial infarction and their functional analyses].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2004 Nov;49(14):2215-21. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2004. PMID: 15559305 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Powerful identification of cis-regulatory SNPs in human primary monocytes using allele-specific gene expression.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52260. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052260. Epub 2012 Dec 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300628 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of a cross-loci regulation network identifies App as a gene regulating insulin secretion from pancreatic islets.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(12):e1003107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003107. Epub 2012 Dec 6. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23236292 Free PMC article.
-
Extent of differential allelic expression of candidate breast cancer genes is similar in blood and breast.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(6):R88. doi: 10.1186/bcr2458. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 20003265 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroscience in the era of functional genomics and systems biology.Nature. 2009 Oct 15;461(7266):908-15. doi: 10.1038/nature08537. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19829370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of brain transcriptional variation reproduced in peripheral blood: an approach for mapping brain expression traits.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Nov 15;18(22):4415-27. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp397. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19692348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International HapMap Consortium The International HapMap Project. Nature. 2003;426:789–796. - PubMed
-
- Cheung VG, Spielman RS. The genetics of variation in gene expression. Nature Genet. 2002;32:522–525. - PubMed
-
- Cheung VG, et al. Natural variation in human gene expression assessed in ymphoblastoid cells. Nature Genet. 2003;33:422–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

