Histone variant H2A.Z marks the 5' ends of both active and inactive genes in euchromatin
- PMID: 16239142
- PMCID: PMC2039754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.002
Histone variant H2A.Z marks the 5' ends of both active and inactive genes in euchromatin
Erratum in
- Cell. 2008 Jul 11;134(1):188
Abstract
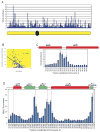
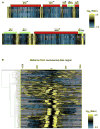
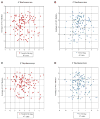
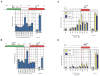
In S. cerevisiae, histone variant H2A.Z is deposited in euchromatin at the flanks of silent heterochromatin to prevent its ectopic spread. We show that H2A.Z nucleosomes are found at promoter regions of nearly all genes in euchromatin. They generally occur as two positioned nucleosomes that flank a nucleosome-free region (NFR) that contains the transcription start site. Astonishingly, enrichment at 5' ends is observed not only at actively transcribed genes but also at inactive loci. Mutagenesis of a typical promoter revealed a 22 bp segment of DNA sufficient to program formation of a NFR flanked by two H2A.Z nucleosomes. This segment contains a binding site of the Myb-related protein Reb1 and an adjacent dT:dA tract. Efficient deposition of H2A.Z is further promoted by a specific pattern of histone H3 and H4 tail acetylation and the bromodomain protein Bdf1, a component of the Swr1 remodeling complex that deposits H2A.Z.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A protein complex containing the conserved Swi2/Snf2-related ATPase Swr1p deposits histone variant H2A.Z into euchromatin.PLoS Biol. 2004 May;2(5):E131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020131. Epub 2004 Mar 23. PLoS Biol. 2004. PMID: 15045029 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H2A.Z regulats transcription and is partially redundant with nucleosome remodeling complexes.Cell. 2000 Oct 27;103(3):411-22. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00133-1. Cell. 2000. PMID: 11081628
-
Conserved histone variant H2A.Z protects euchromatin from the ectopic spread of silent heterochromatin.Cell. 2003 Mar 7;112(5):725-36. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00123-5. Cell. 2003. PMID: 12628191
-
Patterning chromatin: form and function for H2A.Z variant nucleosomes.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006 Apr;16(2):119-24. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2006.02.005. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006. PMID: 16503125 Review.
-
The specificity of H2A.Z occupancy in the yeast genome and its relationship to transcription.Curr Genet. 2020 Oct;66(5):939-944. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01087-7. Epub 2020 Jun 14. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32537667 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into histone exchange by human SRCAP complex.Cell Discov. 2024 Feb 8;10(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41421-023-00640-1. Cell Discov. 2024. PMID: 38331872 Free PMC article.
-
Foxa2 and H2A.Z mediate nucleosome depletion during embryonic stem cell differentiation.Cell. 2012 Dec 21;151(7):1608-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.018. Cell. 2012. PMID: 23260146 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Dynamics and Transcriptional Control of Circadian Rhythms in Arabidopsis.Genes (Basel). 2020 Oct 6;11(10):1170. doi: 10.3390/genes11101170. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33036236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide, as opposed to local, antisilencing is mediated redundantly by the euchromatic factors Set1 and H2A.Z.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 16;104(42):16609-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700914104. Epub 2007 Oct 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17925448 Free PMC article.
-
VivosX, a disulfide crosslinking method to capture site-specific, protein-protein interactions in yeast and human cells.Elife. 2018 Aug 9;7:e36654. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36654. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30091702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angermayr M, Oechsner U, Bandlow W. Reb1p-dependent DNA bending effects nucleosome positioning and constitutive transcription at the yeast profilin promoter. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:17918–17926. - PubMed
-
- Chu S, DeRisi J, Eisen M, Mulholland J, Botstein D, Brown PO, Herskowitz I. The transcriptional program of sporulation in budding yeast. Science. 1998;282:699–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

