Dominant-negative mutant phenotypes and the regulation of translation elongation factor 2 levels in yeast
- PMID: 16214807
- PMCID: PMC1253829
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki882
Dominant-negative mutant phenotypes and the regulation of translation elongation factor 2 levels in yeast
Abstract
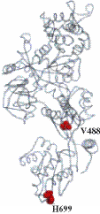
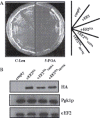
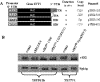
The eukaryotic translation elongation factor 2 (eEF2), a member of the G-protein superfamily, catalyzes the post-peptidyl transferase translocation of deacylated tRNA and peptidyl tRNA to the ribosomal E- and P-sites. eEF2 is modified by a unique post-translational modification: the conversion of His699 to diphthamide at the tip of domain IV, the region proposed to mimic the anticodon of tRNA. Structural models indicate a hinge is important for conformational changes in eEF2. Mutations of V488 in the hinge region and H699 in the tip of domain IV produce non-functional mutants that when co-expressed with the wild-type eEF2 result in a dominant-negative growth phenotype in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This phenotype is linked to reduced levels of the wild-type protein, as total eEF2 levels are unchanged. Changes in the promoter, 5'-untranslated region (5'-UTR) or 3'-UTR of the EFT2 gene encoding eEF2 do not allow overexpression of the protein, showing that eEF2 levels are tightly regulated. The H699K mutant, however, also alters translation phenotypes. The observed regulation suggests that the cell needs an optimum amount of active eEF2 to grow properly. This provides information about a new mechanism by which translation is efficiently maintained.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Translation elongation factor 2 anticodon mimicry domain mutants affect fidelity and diphtheria toxin resistance.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 27;281(43):32639-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607076200. Epub 2006 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16950777
-
Tight interaction of eEF2 in the presence of Stm1 on ribosome.J Biochem. 2018 Mar 1;163(3):177-185. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvx070. J Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29069440
-
Chaperone Function of Hgh1 in the Biogenesis of Eukaryotic Elongation Factor 2.Mol Cell. 2019 Apr 4;74(1):88-100.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.01.034. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30876804
-
Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 (eEF2): its regulation and peptide chain elongation.Cell Biochem Funct. 2011 Apr;29(3):227-34. doi: 10.1002/cbf.1740. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Cell Biochem Funct. 2011. PMID: 21394738 Review.
-
SSD1 modifies phenotypes of Elongator mutants.Curr Genet. 2020 Jun;66(3):481-485. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-01048-9. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 31776648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations in the G-domain of Ski7 cause specific dysfunction in non-stop decay.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 6;6:29295. doi: 10.1038/srep29295. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27381255 Free PMC article.
-
Selection systems based on dominant-negative transcription factors for precise genetic engineering.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):e183. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq708. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20702421 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved eEF2 coding variant in SCA26 leads to loss of translational fidelity and increased susceptibility to proteostatic insult.Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Dec 15;21(26):5472-83. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds392. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2012. PMID: 23001565 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and Regulation of Protein Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2016 May;203(1):65-107. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186221. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27183566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular cloning of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) elongation factor 2 (EF-2): sequence analysis and its expression on the ovarian maturation stage.Mol Biol Rep. 2008 Sep;35(3):431-8. doi: 10.1007/s11033-007-9103-5. Epub 2007 Jul 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2008. PMID: 17629788
References
-
- Hershey J.W.B., Merrick W.C. Pathway and Mechanism of Initiation of Protein Synthesis. In: Sonenberg N., Hershey J.W.B., Mathews M.B., editors. Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2000. pp. 33–88.
-
- Merrick W.C., Nyborg J. The Protein Biosynthesis Elongation Cycle. In: Sonenberg N., Hershey J.W.B., Mathews M.B., editors. Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2000. pp. 89–126.
-
- Welch E.M., Wang W., Peltz S.W. Translation Termination: It's Not the End of the Story. In: Sonenberg N., Hershey J.W.B., Mathews M.B., editors. Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2000. pp. 467–485.
-
- Proud C.G. Regulation of mRNA translation. Essays Biochem. 2001;37:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Huang Y.S., Richter J.D. Regulation of local mRNA translation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004;16:308–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

