Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate attachment and entry of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 virions into CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 16188972
- PMCID: PMC1235841
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.20.12692-12702.2005
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate attachment and entry of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 virions into CD4+ T cells
Abstract
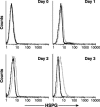
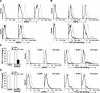
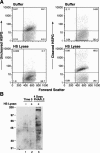
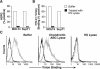
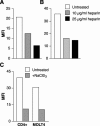
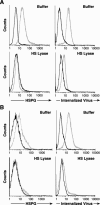
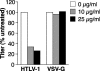
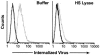
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) are used by a number of viruses to facilitate entry into host cells. For the retrovirus human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1), it has recently been reported that HSPGs are critical for efficient binding of soluble HTLV-1 SU and the entry of HTLV pseudotyped viruses into non-T cells. However, the primary in vivo targets of HTLV-1, CD4(+) T cells, have been reported to express low or undetectable levels of HSPGs. For this study, we reexamined the expression of HSPGs in CD4(+) T cells and examined their role in HTLV-1 attachment and entry. We observed that while quiescent primary CD4(+) T cells do not express detectable levels of HSPGs, HSPGs are expressed on primary CD4(+) T cells following immune activation. Enzymatic modification of HSPGs on the surfaces of either established CD4(+) T-cell lines or primary CD4(+) T cells dramatically reduced the binding of both soluble HTLV-1 SU and HTLV-1 virions. HSPGs also affected the efficiency of HTLV-1 entry, since blocking the interaction with HSPGs markedly reduced both the internalization of HTLV-1 virions and the titer of HTLV-1 pseudotyped viral infection in CD4(+) T cells. Thus, HSPGs play a critical role in the binding and entry of HTLV-1 into CD4(+) T cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-2 use different receptor complexes to enter T cells.J Virol. 2006 Sep;80(17):8291-302. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00389-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16912281 Free PMC article.
-
The receptor complex associated with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 3 (HTLV-3) Env-mediated binding and entry is distinct from, but overlaps with, the receptor complexes of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2.J Virol. 2009 May;83(10):5244-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02285-08. Epub 2009 Mar 11. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19279090 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein gp46 interacts with cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(18):9922-30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.18.9922-9930.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12941902 Free PMC article.
-
Current concepts regarding the HTLV-1 receptor complex.Retrovirology. 2010 Nov 29;7:99. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-99. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 21114861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Free versus Cell-to-Cell Infection by Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 and Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1: Exploring the Link among Viral Source, Viral Trafficking, and Viral Replication.J Virol. 2016 Aug 12;90(17):7607-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00407-16. Print 2016 Sep 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27334587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spermatozoa capture HIV-1 through heparan sulfate and efficiently transmit the virus to dendritic cells.J Exp Med. 2009 Nov 23;206(12):2717-33. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091579. Epub 2009 Oct 26. J Exp Med. 2009. PMID: 19858326 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 transmission and spread.Viruses. 2011 Jul;3(7):1131-65. doi: 10.3390/v3071131. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evasion of a Human Cytomegalovirus Entry Inhibitor with Potent Cysteine Reactivity Is Concomitant with the Utilization of a Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan-Independent Route of Entry.J Virol. 2020 Mar 17;94(7):e02012-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02012-19. Print 2020 Mar 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31941787 Free PMC article.
-
Heparan sulfate proteoglycan-mediated dynamin-dependent transport of neural stem cell exosomes in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model.Eur J Neurosci. 2021 Feb;53(3):706-719. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14974. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Eur J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32939863 Free PMC article.
-
HBZ upregulates myoferlin expression to facilitate HTLV-1 infection.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Feb 24;19(2):e1011202. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011202. eCollection 2023 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36827461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altmeyer, R. 2004. Virus attachment and entry offer numerous targets for antiviral therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 10:3701-3712. - PubMed
-
- Argyris, E. G., E. Acheampong, G. Nunnari, M. Mukhtar, K. J. Williams, and R. J. Pomerantz. 2003. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enters primary human brain microvascular endothelial cells by a mechanism involving cell surface proteoglycans independent of lipid rafts. J. Virol. 77:12140-12151. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barth, H., C. Schafer, M. I. Adah, F. Zhang, R. J. Linhardt, H. Toyoda, A. Kinoshita-Toyoda, T. Toida, T. H. Van Kuppevelt, E. Depla, F. Von Weizsacker, H. E. Blum, and T. F. Baumert. 2003. Cellular binding of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 278:41003-41012. - PubMed
-
- Bernard, K. A., W. B. Klimstra, and R. E. Johnston. 2000. Mutations in the E2 glycoprotein of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus confer heparan sulfate interaction, low morbidity, and rapid clearance from blood of mice. Virology 276:93-103. - PubMed
-
- Bernfield, M., M. Gotte, P. W. Park, O. Reizes, M. L. Fitzgerald, J. Lincecum, and M. Zako. 1999. Functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68:729-777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

