Oncogenic transformation by inhibitor-sensitive and -resistant EGFR mutants
- PMID: 16187797
- PMCID: PMC1240052
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020313
Oncogenic transformation by inhibitor-sensitive and -resistant EGFR mutants
Erratum in
-
Correction: Oncogenic Transformation by Inhibitor-Sensitive and -Resistant EGFR Mutants.PLoS Med. 2024 Sep 16;21(9):e1004470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004470. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Med. 2024. PMID: 39284164 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Somatic mutations in the kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase gene EGFR are common in lung adenocarcinoma. The presence of mutations correlates with tumor sensitivity to the EGFR inhibitors erlotinib and gefitinib, but the transforming potential of specific mutations and their relationship to drug sensitivity have not been described.
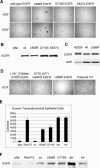
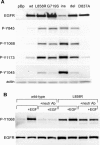
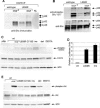
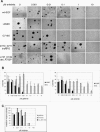
Methods and findings: Here, we demonstrate that EGFR active site mutants are oncogenic. Mutant EGFR can transform both fibroblasts and lung epithelial cells in the absence of exogenous epidermal growth factor, as evidenced by anchorage-independent growth, focus formation, and tumor formation in immunocompromised mice. Transformation is associated with constitutive autophosphorylation of EGFR, Shc phosphorylation, and STAT pathway activation. Whereas transformation by most EGFR mutants confers on cells sensitivity to erlotinib and gefitinib, transformation by an exon 20 insertion makes cells resistant to these inhibitors but more sensitive to the irreversible inhibitor CL-387,785.
Conclusion: Oncogenic transformation of cells by different EGFR mutants causes differential sensitivity to gefitinib and erlotinib. Treatment of lung cancers harboring EGFR exon 20 insertions may therefore require the development of alternative kinase inhibition strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
The need for an individual approach to lung cancer treatment.PLoS Med. 2006 Apr;3(4):e206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030206. Epub 2006 Apr 25. PLoS Med. 2006. PMID: 16626260 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain.PLoS Med. 2005 Mar;2(3):e73. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020073. Epub 2005 Feb 22. PLoS Med. 2005. PMID: 15737014 Free PMC article.
-
MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 26;104(52):20932-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710370104. Epub 2007 Dec 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18093943 Free PMC article.
-
Combined vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) blockade inhibits tumor growth in xenograft models of EGFR inhibitor resistance.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 May 15;15(10):3484-94. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2904. Epub 2009 May 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19447865 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway.Clin Lung Cancer. 2009 Jul;10(4):281-9. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2009.n.039. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19632948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activating and resistance mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: role in clinical response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncogene. 2009 Aug;28 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S24-31. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.198. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19680293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Customised, Individualised Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC).Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2013 May;13(2):202-17. doi: 10.12816/0003225. Epub 2013 May 9. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2013. PMID: 23862025 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor signals regulate dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jun 6;16:354. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2392-0. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27268079 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of osimertinib-resistant epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR-T790M/C797S.Chem Sci. 2019 Oct 4;10(46):10789-10801. doi: 10.1039/c9sc03445e. eCollection 2019 Dec 14. Chem Sci. 2019. PMID: 31857889 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insight and Development of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Molecules. 2022 Jan 26;27(3):819. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030819. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research Advances of EGFR-TP53 Co-mutation in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 Mar 20;25(3):174-182. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.101.06. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35340160 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Yarden Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. Signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(Suppl 4):S3–8. - PubMed
-
- Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TP, Ward CW, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor: Mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284:31–53. - PubMed
-
- Boerner JL, Danielsen A, Maihle NJ. Ligand-independent oncogenic signaling by the epidermal growth factor receptor: v-ErbB as a paradigm. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284:111–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

