Activation of the peripheral endocannabinoid system in human obesity
- PMID: 16186383
- PMCID: PMC2228268
- DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.54.10.2838
Activation of the peripheral endocannabinoid system in human obesity
Abstract
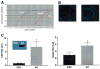
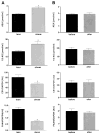
Obesity is the main risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes. Activation of the central endocannabinoid system increases food intake and promotes weight gain. Blockade of the cannabinoid type 1 (CB-1) receptor reduces body weight in animals by central and peripheral actions; the role of the peripheral endocannabinoid system in human obesity is now being extensively investigated. We measured circulating endocannabinoid concentrations and studied the expression of CB-1 and the main degrading enzyme, fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), in adipose tissue of lean (n = 20) and obese (n = 20) women and after a 5% weight loss in a second group of women (n = 17). Circulating levels of anandamide and 1/2-arachidonoylglycerol were increased by 35 and 52% in obese compared with lean women (P < 0.05). Adipose tissue mRNA levels were reduced by -34% for CB-1 and -59% for FAAH in obese subjects (P < 0.05). A strong negative correlation was found between FAAH expression in adipose tissue and circulating endocannabinoids. Circulating endocannabinoids and CB-1 or FAAH expression were not affected by 5% weight loss. The expression of CB-1 and FAAH was increased in mature human adipocytes compared with in preadipocytes and was found in several human tissues. Our findings support the presence of a peripheral endocannabinoid system that is upregulated in human obesity.
Figures
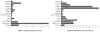
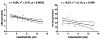
Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of the peripheral and adipose tissue endocannabinoid system in human abdominal obesity.Diabetes. 2006 Nov;55(11):3053-60. doi: 10.2337/db06-0812. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 17065342 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose tissue endocannabinoid system gene expression: depot differences and effects of diet and exercise.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Oct 28;10:194. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-194. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22035053 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of dietary fat intake on the endocannabinoid system in lean and obese subjects.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014 May;22(5):E70-6. doi: 10.1002/oby.20728. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014. PMID: 24616451 Clinical Trial.
-
The endocannabinoid system: a new target for the regulation of energy balance and metabolism.Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2007 Jun;6(2):46-50. doi: 10.1097/HPC.0b013e318057d4b4. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17667864 Review.
-
Investigations of the endocannabinoid system in adipose tissue: effects of obesity/ weight loss and treatment options.Dan Med Bull. 2011 Apr;58(4):B4269. Dan Med Bull. 2011. PMID: 21466769 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic endocannabinoid system stimulation induces muscle macrophage and lipid accumulation in type 2 diabetic mice independently of metabolic endotoxaemia.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055963. Epub 2013 Feb 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23393605 Free PMC article.
-
Links between central CB1-receptor availability and peripheral endocannabinoids in patients with first episode psychosis.NPJ Schizophr. 2020 Aug 26;6(1):21. doi: 10.1038/s41537-020-00110-7. NPJ Schizophr. 2020. PMID: 32848142 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral, Metabolic, and Immune Consequences of Chronic Alcohol or Cannabinoids on HIV/AIDs: Studies in the Non-Human Primate SIV Model.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;10(2):217-32. doi: 10.1007/s11481-015-9599-8. Epub 2015 Mar 21. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25795088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating endocannabinoid concentrations during orthostatic stress.Clin Auton Res. 2009 Dec;19(6):343-6. doi: 10.1007/s10286-009-0026-1. Clin Auton Res. 2009. PMID: 19756829
-
The endocrine disruptor DEHP and the ECS: analysis of a possible crosstalk.Endocr Connect. 2020 Feb;9(2):101-110. doi: 10.1530/EC-19-0548. Endocr Connect. 2020. PMID: 31910153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson PW, D’Agostino RB, Sullivan L, Parise H, Kannel WB. Overweight and obesity as determinants of cardiovascular risk: the Framingham experience. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:1867–1872. - PubMed
-
- Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R. Body mass index, waist circumference, and health risk: evidence in support of current National Institutes of Health guidelines. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:2074–2079. - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Rastas M, Salminen V, Uusitupa M. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1343–1350. - PubMed
-
- Sjöström L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M, Torgerson J, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, Dahlgren S, Larsson B, Narbro K, Sjöström CD, Sullivan M, Wedel H. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2683–2693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

