Inorganic polyphosphate in the social life of Myxococcus xanthus: motility, development, and predation
- PMID: 16174737
- PMCID: PMC1224657
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506520102
Inorganic polyphosphate in the social life of Myxococcus xanthus: motility, development, and predation
Abstract
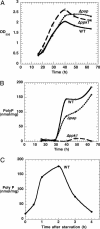
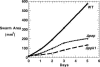
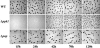
Inorganic polyphosphate (poly P), a polymer of tens or hundreds of phosphate residues linked by high-energy, ATP-like bonds, is found in all organisms and performs a wide variety of functions. Myxococcus xanthus, a social bacterium that feeds on other bacteria and forms fruiting bodies and spores, depends on poly P for motility, development, and nutritional predation. Two poly P metabolizing enzymes were studied in M. xanthus: poly P kinase 1, which synthesizes poly P reversibly from ATP, and poly P:AMP phosphotransferase, which uses poly P as a donor to also reversibly convert AMP to ADP. The null mutant of ppk1 is defective in social motility, overproduces pilin protein on the cell surface, is delayed in fruiting body formation, produces fewer spores, is delayed in germination, and forms far smaller plaques on a lawn of Klebsiella aerogenes. The pap mutant is also impaired in social motility, but shows only slightly reduced abilities in development and predation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polyphosphate Plays a Significant Role in the Maturation of Spores in Myxococcus xanthus.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Jul 1;81(8):248. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03778-7. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38951187
-
Inorganic polyphosphate in Dictyostelium discoideum: influence on development, sporulation, and predation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):2731-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500023102. Epub 2005 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15701689 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate in Bacillus cereus: motility, biofilm formation, and sporulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 7;101(49):17061-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407787101. Epub 2004 Nov 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15572452 Free PMC article.
-
Regulations governing the multicellular lifestyle of Myxococcus xanthus.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Dec;34:104-110. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27648756 Review.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate in the origin and survival of species.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Nov 16;101(46):16085-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406909101. Epub 2004 Nov 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15520374 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acidocalcisomes.Cell Calcium. 2011 Aug;50(2):113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2011.05.012. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Cell Calcium. 2011. PMID: 21752464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enzymatic Characteristics of a Polyphosphate/ATP-NAD Kinase, PanK, from Myxococcus xanthus.Curr Microbiol. 2020 Feb;77(2):173-178. doi: 10.1007/s00284-019-01810-9. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Curr Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31741028
-
Phosphate acquisition components of the Myxococcus xanthus Pho regulon are regulated by both phosphate availability and development.J Bacteriol. 2008 Mar;190(6):1997-2003. doi: 10.1128/JB.01781-07. Epub 2008 Jan 4. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18178740 Free PMC article.
-
Lipolytic enzymes in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2007 Apr;189(8):3072-80. doi: 10.1128/JB.01772-06. Epub 2007 Feb 16. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17307851 Free PMC article.
-
A polyphosphate kinase 1 (ppk1) mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits multiple ultrastructural and functional defects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 27;104(9):3526-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609733104. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360677 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

