MicroRNA biogenesis and function in plants
- PMID: 16144699
- PMCID: PMC5127707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.07.071
MicroRNA biogenesis and function in plants
Abstract
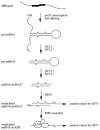
A microRNA (miRNA) is a 21-24 nucleotide RNA product of a non-protein-coding gene. Plants, like animals, have a large number of miRNA-encoding genes in their genomes. The biogenesis of miRNAs in Arabidopsis is similar to that in animals in that miRNAs are processed from primary precursors by at least two steps mediated by RNAse III-like enzymes and that the miRNAs are incorporated into a protein complex named RISC. However, the biogenesis of plant miRNAs consists of an additional step, i.e., the miRNAs are methylated on the ribose of the last nucleotide by the miRNA methyltransferase HEN1. The high degree of sequence complementarity between plant miRNAs and their target mRNAs has facilitated the bioinformatic prediction of miRNA targets, many of which have been subsequently validated. Plant miRNAs have been predicted or confirmed to regulate a variety of processes, such as development, metabolism, and stress responses. A large category of miRNA targets consists of genes encoding transcription factors that play important roles in patterning the plant form.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CARPEL FACTORY, a Dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana.Curr Biol. 2002 Sep 3;12(17):1484-95. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01017-5. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12225663 Free PMC article.
-
Functional mapping of the plant small RNA methyltransferase: HEN1 physically interacts with HYL1 and DICER-LIKE 1 proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Mar 11;43(5):2802-12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv102. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25680966 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation as a crucial step in plant microRNA biogenesis.Science. 2005 Feb 11;307(5711):932-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1107130. Science. 2005. PMID: 15705854 Free PMC article.
-
Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact.Dev Biol. 2006 Jan 1;289(1):3-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.10.036. Epub 2005 Dec 1. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16325172 Review.
-
MicroRNA metabolism in plants.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;320:117-36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75157-1_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18268842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential functions of microRNAs in starch metabolism and development revealed by miRNA transcriptome profiling of cassava cultivars and their wild progenitor.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Feb 4;15:33. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0355-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25648603 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide identification and characterization of microRNAs from castor bean (Ricinus communis L.).PLoS One. 2013 Jul 24;8(7):e69995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069995. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894571 Free PMC article.
-
miRTRAP, a computational method for the systematic identification of miRNAs from high throughput sequencing data.Genome Biol. 2010;11(4):R39. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-4-r39. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20370911 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol: a highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs.Plant Methods. 2007 Oct 12;3:12. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-3-12. Plant Methods. 2007. PMID: 17931426 Free PMC article.
-
A structured viroid RNA serves as a substrate for dicer-like cleavage to produce biologically active small RNAs but is resistant to RNA-induced silencing complex-mediated degradation.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(6):2980-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02339-06. Epub 2007 Jan 3. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17202210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim VN. MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:376–385. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286:950–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

