NF-kappaB RelA phosphorylation regulates RelA acetylation
- PMID: 16135789
- PMCID: PMC1234328
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.18.7966-7975.2005
NF-kappaB RelA phosphorylation regulates RelA acetylation
Abstract
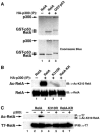
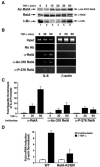
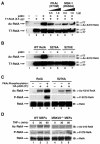
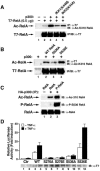
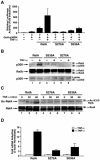
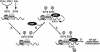
The nuclear functions of NF-kappaB p50/RelA heterodimers are regulated in part by posttranslational modifications of its RelA subunit, including phosphorylation and acetylation. Acetylation at lysines 218, 221, and 310 differentially regulates RelA's DNA binding activity, assembly with IkappaBalpha, and transcriptional activity. However, it remains unclear whether the acetylation is regulated or simply due to stimulus-coupled nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB. Using anti-acetylated lysine 310 RelA antibodies, we detected p300-mediated acetylation of RelA in vitro and in vivo after stimulation of cells with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). Coexpression of catalytically inactive mutants of the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A/mitogen- and stress-activated kinase 1 or IKK1/IKK2, which phosphorylate RelA on serine 276 or serine 536, respectively, sharply inhibited RelA acetylation on lysine 310. Furthermore, phosphorylation of RelA on serine 276 or serine 536 increased assembly of phospho-RelA with p300, which enhanced acetylation on lysine 310. Reconstitution of RelA-deficient murine embryonic fibroblasts with RelA S276A or RelA S536A decreased TNF-alpha-induced acetylation of lysine 310 and expression of the endogenous NF-kappaB-responsive E-selectin gene. These findings indicate that the acetylation of RelA at lysine 310 is importantly regulated by prior phosphorylation of serines 276 and 536. Such phosphorylated and acetylated forms of RelA display enhanced transcriptional activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Essential role of RelA Ser311 phosphorylation by zetaPKC in NF-kappaB transcriptional activation.EMBO J. 2003 Aug 1;22(15):3910-8. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg370. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12881425 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of nuclear factor-kappa B acetylation by coactivator p300 and HIV-1 Tat proteins.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 15;277(7):4973-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107848200. Epub 2001 Dec 5. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11739381
-
Insufficient p65 phosphorylation at S536 specifically contributes to the lack of NF-kappaB activation and transformation in resistant JB6 cells.Carcinogenesis. 2004 Oct;25(10):1991-2003. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh198. Epub 2004 Jun 10. Carcinogenesis. 2004. PMID: 15192014
-
Regulation of NF-kappaB action by reversible acetylation.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;259:208-17; discussion 218-25. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15171256 Review.
-
Regulation of distinct biological activities of the NF-kappaB transcription factor complex by acetylation.J Mol Med (Berl). 2003 Sep;81(9):549-57. doi: 10.1007/s00109-003-0469-0. Epub 2003 Aug 15. J Mol Med (Berl). 2003. PMID: 12920522 Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet factor 4 (CXCL4/PF4) upregulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in gingival fibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 3;12(1):18636. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19850-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36329090 Free PMC article.
-
Dimethyl fumarate inhibits dendritic cell maturation via nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and mitogen stress-activated kinase 1 (MSK1) signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 10;287(33):28017-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.383380. Epub 2012 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22733812 Free PMC article.
-
PKCζ Promotes Breast Cancer Invasion by Regulating Expression of E-cadherin and Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1) via NFκB-p65.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 28;5:12520. doi: 10.1038/srep12520. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26218882 Free PMC article.
-
Polyomavirus ALTOs, but not MTs, downregulate viral early gene expression by activating the NF-κB pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2403133121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2403133121. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39141346
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition protects hearing against acute ototoxicity by activating the Nf-κB pathway.Cell Death Discov. 2015;1:15012-. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.12. Cell Death Discov. 2015. PMID: 26279947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldwin, A. S., Jr. 1996. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:649-683. - PubMed
-
- Berger, S. L. 2002. Histone modifications in transcriptional regulation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12:142-148. - PubMed
-
- Bohuslav, J., L. F. Chen, H. Kwon, Y. Mu, and W. C. Greene. 2004. p53 Induces NF-κB activation by an IκB kinase-independent mechanism involving RSK1 phosphorylation of p65. J. Biol. Chem. 279:26115-26125. - PubMed
-
- Chen, L. F., W. Fischle, E. Verdin, and W. C. Greene. 2001. Duration of nuclear NF-κB action regulated by reversible acetylation. Science 293:1653-1657. - PubMed
-
- Chen, L. F., and W. C. Greene. 2004. Shaping the nuclear action of NF-κB. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5:392-401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
