Hyperphosphorylation regulates the activity of SREBP1 during mitosis
- PMID: 16081540
- PMCID: PMC1187962
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0501494102
Hyperphosphorylation regulates the activity of SREBP1 during mitosis
Abstract
The sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) family of transcription factors controls the biosynthesis of cholesterol and other lipids, and lipid synthesis is critical for cell growth and proliferation. We were, therefore, interested in the expression and activity of SREBPs during the cell cycle. We found that the expression of a number of SREBP-responsive promoter-reporter genes were induced in a SREBP-dependent manner in cells arrested in G2/M. In addition, the mature forms of SREBP1a and SREBP1c were hyperphosphorylated in mitotic cells, giving rise to a phosphoepitope recognized by the mitotic protein monoclonal-2 (MPM-2) antibody. In contrast, SREBP2 was not hyperphosphorylated in mitotic cells and was not recognized by the MPM-2 antibody. The MPM-2 epitope was mapped to the C terminus of mature SREBP1, and the mitosis-specific hyperphosphorylation of SREBP1 depended on this domain of the protein. The transcriptional and DNA-binding activity of SREBP1 was enhanced in cells arrested in G2/M, and these effects depended on the C-terminal domain of the protein. In part, these effects could be explained by our observation that mature SREBP1 was stabilized in G2/M. In agreement with these observations, we found that the synthesis of cholesterol was increased in G2/M-arrested cells. Thus, our results demonstrate that the activity of mature SREBP1 is regulated by phosphorylation during the cell cycle, suggesting that SREBP1 may provide a link between lipid synthesis, proliferation, and cell growth.
Figures
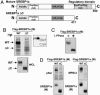
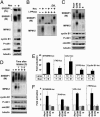

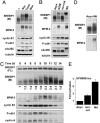
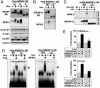
Similar articles
-
Transcription factor sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 regulates scavenger receptor Cla-1 gene expression.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004 Dec;24(12):2358-64. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000147896.69299.85. Epub 2004 Oct 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15486308
-
Cdk1/cyclin B-mediated phosphorylation stabilizes SREBP1 during mitosis.Cell Cycle. 2006 Aug;5(15):1708-18. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.15.3131. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16880739
-
SREBP transcription factors: master regulators of lipid homeostasis.Biochimie. 2004 Nov;86(11):839-48. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.09.018. Biochimie. 2004. PMID: 15589694 Review.
-
SREBP inhibits VEGF expression in human smooth muscle cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Mar 31;342(1):354-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.139. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16480961
-
[Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins and lipid metabolism].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2005 Jan;36(1):29-34. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2005. PMID: 15881340 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Insulin receptor isoform B is required for efficient proinsulin processing in pancreatic β cells.iScience. 2024 May 17;27(7):110017. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110017. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39021804 Free PMC article.
-
Growth factor-induced phosphorylation of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins inhibits sumoylation, thereby stimulating the expression of their target genes, low density lipoprotein uptake, and lipid synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 30;283(22):15224-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800910200. Epub 2008 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18403372 Free PMC article.
-
SREBP1, targeted by miR-18a-5p, modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer via forming a co-repressor complex with Snail and HDAC1/2.Cell Death Differ. 2019 May;26(5):843-859. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0158-8. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 29988076 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3-mediated phosphorylation of serine 73 targets sterol response element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) for proteasomal degradation.Biosci Rep. 2015 Nov 20;36(1):e00284. doi: 10.1042/BSR20150234. Biosci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26589965 Free PMC article.
-
A functional genomics screen reveals a strong synergistic effect between docetaxel and the mitotic gene DLGAP5 that is mediated by the androgen receptor.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 19;9(11):1069. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1115-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30341281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Edwards, P. A., Tabor, D., Kast, H. R. & Venkateswaran, A. (2000) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1529, 103–113. - PubMed
-
- Rawson, R. B., Zelenski, N. G., Nijhawan, D., Ye, J., Sakai, J., Hasan, M. T., Chang, T. Y., Brown, M. S. & Goldstein, J. L. (1997) Mol. Cell 1, 47–57. - PubMed
-
- Sakai, J., Rawson, R. B., Espenshade, P. J., Cheng, D., Seegmiller, A. C., Goldstein, J. L. & Brown, M. S. (1998) Mol. Cell 2, 505–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

