Down-regulation of c-Fos/c-Jun AP-1 dimer activity by sumoylation
- PMID: 16055710
- PMCID: PMC1190241
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.16.6964-6979.2005
Down-regulation of c-Fos/c-Jun AP-1 dimer activity by sumoylation
Abstract
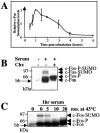
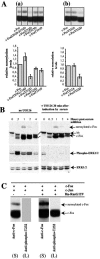
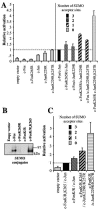
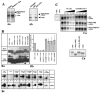
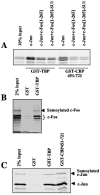
The inducible transcriptional complex AP-1, composed of c-Fos and c-Jun proteins, is crucial for cell adaptation to many environmental changes. While its mechanisms of activation have been extensively studied, how its activity is restrained is poorly understood. We report here that lysine 265 of c-Fos is conjugated by the peptidic posttranslational modifiers SUMO-1, SUMO-2, and SUMO-3 and that c-Jun can be sumoylated on lysine 257 as well as on the previously described lysine 229. Sumoylation of c-Fos preferentially occurs in the context of c-Jun/c-Fos heterodimers. Using nonsumoylatable mutants of c-Fos and c-Jun as well as a chimeric protein mimicking sumoylated c-Fos, we show that sumoylation entails lower AP-1 transactivation activity. Interestingly, single sumoylation at any of the three acceptor sites of the c-Fos/c-Jun dimer is sufficient to substantially reduce transcription activation. The lower activity of sumoylated c-Fos is not due to inhibition of protein entry into the nucleus, accelerated turnover, and intrinsic inability to dimerize or to bind to DNA. Instead, cell fractionation experiments suggest that decreased transcriptional activity of sumoylated c-Fos is associated with specific intranuclear distribution. Interestingly, the phosphorylation of threonine 232 observed upon expression of oncogenically activated Ha-Ras is known to superactivate c-Fos transcriptional activity. We show here that it also inhibits c-Fos sumoylation, revealing a functional antagonism between two posttranslational modifications, each occurring within a different moiety of a bipartite transactivation domain of c-Fos. Finally we report that the sumoylation of c-Fos is a dynamic process that can be reversed via multiple mechanisms. This supports the idea that this modification does not constitute a final inactivation step that necessarily precedes protein degradation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
c-Fos transcriptional activity stimulated by H-Ras-activated protein kinase distinct from JNK and ERK.Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):171-5. doi: 10.1038/371171a0. Nature. 1994. PMID: 8072547
-
Menin uncouples Elk-1, JunD and c-Jun phosphorylation from MAP kinase activation.Oncogene. 2002 Sep 19;21(42):6434-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205822. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12226747
-
A peptide fragment of ependymin neurotrophic factor uses protein kinase C and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase and a functional AP-1 containing c-Jun and c-Fos proteins in mouse NB2a cells.J Neurosci Res. 2003 May 1;72(3):405-16. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10590. J Neurosci Res. 2003. PMID: 12692907
-
Close encounters of many kinds: Fos-Jun interactions that mediate transcription regulatory specificity.Oncogene. 2001 Apr 30;20(19):2438-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204385. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11402339 Review.
-
Distinct roles of Jun : Fos and Jun : ATF dimers in oncogenesis.Oncogene. 2001 Apr 30;20(19):2453-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204239. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11402340 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation-dependent SUMOylation of the transcription factor NF-E2.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044608. Epub 2012 Sep 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22970264 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of c-Jun protein plays an instrumental role in chemoresistance of cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 5;288(27):19321-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.475442. Epub 2013 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23678002 Free PMC article.
-
The bZIP Proteins of Oncogenic Viruses.Viruses. 2020 Jul 14;12(7):757. doi: 10.3390/v12070757. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32674309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An NF-kappaB-dependent role for JunB in the induction of proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-activated bone marrow-derived dendritic cells.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 8;5(3):e9585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009585. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20221401 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and promoter characterization of aldo-keto reductase family 1 B10 gene.Gene. 2009 May 15;437(1-2):39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.02.007. Epub 2009 Feb 21. Gene. 2009. PMID: 19236911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abate, C., D. R. Marshak, and T. Curran. 1991. Fos is phosphorylated by p34cdc2, cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C at multiple sites clustered within regulatory regions. Oncogene 6:2179-2185. - PubMed
-
- Acquaviva, C., F. Brockly, P. Ferrara, G. Bossis, C. Salvat, I. Jariel-Encontre, and M. Piechaczyk. 2001. Identification of a C-terminal tripeptide motif involved in the control of rapid proteasomal degradation of c-Fos proto-oncoprotein during the G(0)-to-S phase transition. Oncogene 20:7563-7572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
