High-affinity interaction of the N-terminal myristoylation motif of the neuronal calcium sensor protein hippocalcin with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
- PMID: 16053445
- PMCID: PMC1276920
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051001
High-affinity interaction of the N-terminal myristoylation motif of the neuronal calcium sensor protein hippocalcin with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Abstract
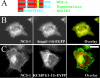
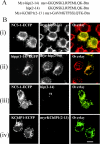
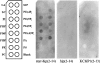
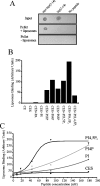
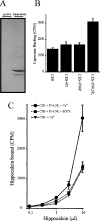
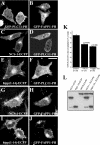
Many proteins are associated with intracellular membranes due to their N-terminal myristoylation. Not all myristoylated proteins have the same localization within cells, indicating that other factors must determine their membrane targeting. The NCS (neuronal calcium sensor) proteins are a family of Ca2+-binding proteins with diverse functions. Most members of the family are N-terminally myristoylated and are either constitutively membrane-bound or have a Ca2+/myristoyl switch that allows their reversible membrane association in response to Ca2+ signals. In the case of hippocalcin and NCS-1, or alternatively KChIP1 (K+ channel-interacting protein 1), their N-terminal myristoylation motifs are sufficient for targeting to distinct organelles. We have shown that an N-terminal myristoylated hippocalcin peptide is able to specifically reproduce the membrane targeting of hippocalcin/NCS-1 when introduced into permeabilized cells. The peptide binds to liposomes containing phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] with high affinity (K(d) 50 nM). Full-length hippocalcin also bound preferentially to liposomes supplemented with PtdIns(4,5)P2. Co-expression of hippocalcin-(1-14)-ECFP (enhanced cyan fluorescent protein) or NCS-1-ECFP partially displaced the expressed PH (pleckstrin homology) domain of phospholipase delta1 from the plasma membrane in live cells, indicating that they have a higher affinity for PtdIns(4,5)P2 than does this PH domain. The Golgi localization of the PH domain of FAPP1 (four-phosphate-adaptor protein 1), which binds to phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, was unaffected. The localization of NCS-1 and hippocalcin is likely to be determined, therefore, by their interaction with PtdIns(4,5)P2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Residues within the myristoylation motif determine intracellular targeting of the neuronal Ca2+ sensor protein KChIP1 to post-ER transport vesicles and traffic of Kv4 K+ channels.J Cell Sci. 2003 Dec 1;116(Pt 23):4833-45. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00803. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 14600268
-
Differential use of myristoyl groups on neuronal calcium sensor proteins as a determinant of spatio-temporal aspects of Ca2+ signal transduction.J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 19;277(16):14227-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111750200. Epub 2002 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11836243
-
Membrane Binding of Neuronal Calcium Sensor-1: Highly Specific Interaction with Phosphatidylinositol-3-Phosphate.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 21;10(2):164. doi: 10.3390/biom10020164. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31973069 Free PMC article.
-
Role of myristoylation in the intracellular targeting of neuronal calcium sensor (NCS) proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Oct;31(Pt 5):963-5. doi: 10.1042/bst0310963. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 14505460 Review.
-
The neuronal calcium sensor family of Ca2+-binding proteins.Biochem J. 2001 Jan 1;353(Pt 1):1-12. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11115393 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of VILIP-1 and VILIP-3 binding to phospholipid monolayers.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 3;9(4):e93948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093948. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24699524 Free PMC article.
-
Ca(2+) sensor proteins in dendritic spines: a race for Ca(2+).Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 May 8;5:61. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00061. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22586368 Free PMC article.
-
The diversity of calcium sensor proteins in the regulation of neuronal function.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Aug;2(8):a004085. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a004085. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20668007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visinin-like proteins (VSNLs): interaction partners and emerging functions in signal transduction of a subfamily of neuronal Ca2+ -sensor proteins.Cell Tissue Res. 2009 Feb;335(2):301-16. doi: 10.1007/s00441-008-0716-3. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Cell Tissue Res. 2009. PMID: 18989702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct mechanism of Tb3+ and Eu3+ binding to NCS1.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2023 Mar 29;25(13):9500-9512. doi: 10.1039/d2cp05765d. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2023. PMID: 36938969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Resh M. D. Fatty acylation of proteins: new insights into membrane targeting of myristoylated and palmitoylated proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1999;1451:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Burgoyne R. D., O'Callaghan D. W., Hasdemir B., Haynes L. P., Tepikin A. V. Neuronal calcium sensor proteins: multitalented regulators of neuronal function. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:203–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

