Regulation of ERK1 gene expression by coactivator proteins
- PMID: 16050810
- PMCID: PMC1316299
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050542
Regulation of ERK1 gene expression by coactivator proteins
Abstract
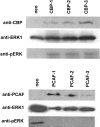
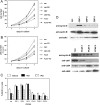
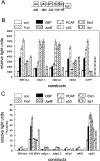
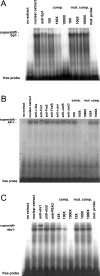
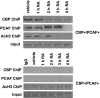
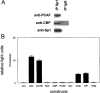
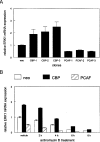
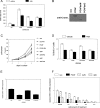
RARs (retinoic acid receptors) mediate the effect of their ligand RA (retinoic acid) on gene expression. We previously showed that RA inhibited cellular proliferation in part by decreasing expression of the mitogen activated protein kinase ERK1 (extracellular signal regulated kinase 1). However, the mechanism by which RA regulates ERK1 expression is largely uncharacterized. The present study characterizes coactivator-mediated regulation of RA target gene expression by analysing ERK1 promoter activation. CBP (CREB-binding protein) and PCAF (p300/CBP associated factor) are transcriptional coactivators that interact with nuclear hormone receptors such as RARs. CBP and PCAF differentially regulated ERK1 expression in stable clones. CBP clones expressed higher ERK1 protein levels, proliferated faster in culture and were resistant to RA-mediated growth inhibition. PCAF clones expressed lower levels of ERK1 protein and cells grew more slowly than controls. CBP and PCAF regulation of the ERK1 promoter was dependent on two Sp1 (specificity protein 1) sites located between -86 and -115 bp. Immunoprecipitation and yeast two-hybrid analysis revealed that PCAF interacted with Sp1 via CBP. A putative p53 binding site at -360 bp functioned as a major repressor of ERK1 promoter activity even in the absence of exogenous p53 expression. CBP and PCAF occupancy of the proximal ERK1 promoter was dramatically decreased by RA treatment. PCAF mediated inhibition of ERK1 expression was due to decreased stability of the kinase mRNA. We conclude that CBP and PCAF coactivators mediate ERK1 gene expression at both the transcriptional and post-transcriptional level.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retinoids and carnosol suppress cyclooxygenase-2 transcription by CREB-binding protein/p300-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Cancer Res. 2002 May 1;62(9):2522-30. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11980644
-
Extracellular signals regulate rapid coactivator recruitment at AP-1 sites by altered phosphorylation of both CREB binding protein and c-jun.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jul;28(13):4240-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01489-07. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18443043 Free PMC article.
-
The acetyltransferase p300/CBP-associated factor is a p53 target gene in breast tumor cells.Neoplasia. 2004 May-Jun;6(3):187-94. doi: 10.1593/neo.3292. Neoplasia. 2004. PMID: 15153330 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the human involucrin gene promoter by co-activator proteins.Biochem J. 2004 Jul 1;381(Pt 1):267-73. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031653. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15025563 Free PMC article.
-
PCAF fine-tunes hepatic metabolic syndrome, inflammatory disease, and cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Dec;22(12):5787-5800. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13877. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30216660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting combinatorial binding of transcription factors to regulatory elements in the human genome by association rule mining.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Nov 15;8:445. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-445. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 18005433 Free PMC article.
-
DUSP4 appears to be a highly localized endogenous inhibitor of epileptic signaling in human neocortex.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Nov;145:105073. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105073. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32890776 Free PMC article.
-
Suv39H1 and HP1gamma are responsible for chromatin-mediated HIV-1 transcriptional silencing and post-integration latency.EMBO J. 2007 Jan 24;26(2):424-35. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601517. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17245432 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ret/PTC 1 rearrangement on transcription and post-transcriptional regulation in a papillary thyroid carcinoma model.Mol Cancer. 2006 Dec 11;5:70. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-70. Mol Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17156473 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the B-Raf/Mek/Erk MAP kinase pathway as a target for all-trans retinoic acid during skin cancer promotion.Mol Cancer. 2009 May 11;8:27. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-27. Mol Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19432991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kastner P., Mark M., Chambon P. Nonsteroid nuclear receptors: what are genetic studies telling us about their role in real life? Cell. 1995;83:859–869. - PubMed
-
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995;83:841–850. - PubMed
-
- Leblanc B. P., Stunnenberg H. G. 9 cis retinoic acid signaling: changing partners causes some excitement. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1811–1816. - PubMed
-
- Chakravarti D., LaMorte V. J., Nelson M. C., Nakajima T., Schulman I. G., Juguilon H., Montminy M., Evans R. M. Role of CBP/p300 in nuclear receptor signaling. Nature (London) 1996;383:99–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

