Isoform-selective effects of the depletion of ADP-ribosylation factors 1-5 on membrane traffic
- PMID: 16030262
- PMCID: PMC1237059
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1042
Isoform-selective effects of the depletion of ADP-ribosylation factors 1-5 on membrane traffic
Abstract
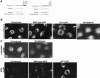
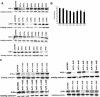
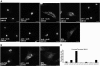
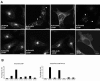
The ADP-ribosylation factors (Arfs) are six proteins within the larger Arf family and Ras superfamily that regulate membrane traffic. Arfs all share numerous biochemical activities and have very similar specific activities. The use of dominant mutants and brefeldin A has been important to the discovery of the cellular functions of Arfs but lack specificity between Arf isoforms. We developed small interference RNA constructs capable of specific depletion of each of the cytoplasmic human Arfs to examine the specificity of Arfs in live cells. No single Arf was required for any step of membrane traffic examined in HeLa cells. However, every combination of the double knockdowns of Arf1, Arf3, Arf4, and Arf5 yielded a distinct pattern of defects in secretory and endocytic traffic, demonstrating clear specificity for Arfs at multiple steps. These results suggest that the cooperation of two Arfs at the same site may be a general feature of Arf signaling and provide candidates at several cellular locations that when paired with data on the localization of the many different Arf guanine nucleotide exchange factors, Arf GTPase activating proteins, and effectors will aid in the description of the mechanisms of specificity in this highly conserved and primordial family of regulatory GTPases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enterovirus Infection Induces Massive Recruitment of All Isoforms of Small Cellular Arf GTPases to the Replication Organelles.J Virol. 2020 Dec 22;95(2):e01629-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01629-20. Print 2020 Dec 22. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 33087467 Free PMC article.
-
Class II Arfs require a brefeldin-A-sensitive factor for Golgi association.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Sep 10;530(1):301-306. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32828303
-
ARF1 and ARF4 regulate recycling endosomal morphology and retrograde transport from endosomes to the Golgi apparatus.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Aug;24(16):2570-81. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-04-0197. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23783033 Free PMC article.
-
Arf family GTPases: roles in membrane traffic and microtubule dynamics.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1269-72. doi: 10.1042/BST0331269. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246095 Review.
-
Molecular aspects of the cellular activities of ADP-ribosylation factors.Sci STKE. 2000 Nov 21;2000(59):re1. doi: 10.1126/stke.2000.59.re1. Sci STKE. 2000. PMID: 11752622 Review.
Cited by
-
Morpho-functional architecture of the Golgi complex of neuroendocrine cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013 Mar 28;4:41. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00041. eCollection 2013. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013. PMID: 23543640 Free PMC article.
-
Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli modulates an ARF6:Rab35 signaling axis to prevent recycling endosome maturation during infection.J Mol Biol. 2016 Aug 28;428(17):3399-407. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.05.023. Epub 2016 May 31. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27261256 Free PMC article.
-
A neurodevelopmental disorder associated with an activating de novo missense variant in ARF1.Hum Mol Genet. 2023 Mar 20;32(7):1162-1174. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac279. Hum Mol Genet. 2023. PMID: 36345169 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of small GTPases at the Golgi apparatus.Small GTPases. 2012 Apr-Jun;3(2):80-90. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.19842. Small GTPases. 2012. PMID: 22790194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impairment of protein trafficking upon overexpression and mutation of optineurin.PLoS One. 2010 Jul 12;5(7):e11547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011547. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20634958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balch, W. E., Kahn, R. A., and Schwaninger, R. (1992). ADP-ribosylation factor is required for vesicular trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and the cis-Golgi compartment. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 13053–13061. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe, C., Orci, L., Yeung, T., Hosobuchi, M., Hamamoto, S., Salama, N., Rexach, M. F., Ravazzola, M., Amherdt, M., and Schekman, R. (1994). COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 77, 895–907. - PubMed
-
- Brown, H. A., Gutowski, S., Kahn, R. A., and Sternweis, P. C. (1995). Partial purification and characterization of Arf-sensitive phospholipase D from porcine brain. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 14935–14943. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp, T. R., Bernards, R., and Agami, R. (2002). A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296, 550–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

