H++: a server for estimating pKas and adding missing hydrogens to macromolecules
- PMID: 15980491
- PMCID: PMC1160225
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki464
H++: a server for estimating pKas and adding missing hydrogens to macromolecules
Abstract
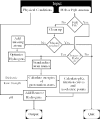
The structure and function of macromolecules depend critically on the ionization (protonation) states of their acidic and basic groups. A number of existing practical methods predict protonation equilibrium pK constants of macromolecules based upon their atomic resolution Protein Data Bank (PDB) structures; the calculations are often performed within the framework of the continuum electrostatics model. Unfortunately, these methodologies are complex, involve multiple steps and require considerable investment of effort. Our web server http://biophysics.cs.vt.edu/H++ provides access to a tool that automates this process, allowing both experts and novices to quickly obtain estimates of pKs as well as other related characteristics of biomolecules such as isoelectric points, titration curves and energies of protonation microstates. Protons are added to the input structure according to the calculated ionization states of its titratable groups at the user-specified pH; the output is in the PQR (PDB + charges + radii) format. In addition, corresponding coordinate and topology files are generated in the format supported by the molecular modeling package AMBER. The server is intended for a broad community of biochemists, molecular modelers, structural biologists and drug designers; it can also be used as an educational tool in biochemistry courses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patch Finder Plus (PFplus): a web server for extracting and displaying positive electrostatic patches on protein surfaces.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W526-30. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm401. Epub 2007 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17537808 Free PMC article.
-
PDB2PQR: an automated pipeline for the setup of Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatics calculations.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jul 1;32(Web Server issue):W665-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh381. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15215472 Free PMC article.
-
H++ 3.0: automating pK prediction and the preparation of biomolecular structures for atomistic molecular modeling and simulations.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(Web Server issue):W537-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks375. Epub 2012 May 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22570416 Free PMC article.
-
The HADDOCK2.4 web server for integrative modeling of biomolecular complexes.Nat Protoc. 2024 Nov;19(11):3219-3241. doi: 10.1038/s41596-024-01011-0. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Nat Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38886530 Review.
-
Electrostatic effects in macromolecules: fundamental concepts and practical modeling.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998 Apr;8(2):211-7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(98)80041-9. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998. PMID: 9631295 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of a family 5 glycoside hydrolase suggests an induced-fit enzymatic mechanism.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 1;6:23473. doi: 10.1038/srep23473. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27032335 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha induces a mechanical allosteric regulation and changes in internal dynamics.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003012. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003012. Epub 2013 Apr 18. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23637584 Free PMC article.
-
Streptomyces coelicolor macrodomain hydrolase SCO6735 cleaves thymidine-linked ADP-ribosylation of DNA.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Aug 8;20:4337-4350. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.002. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36051881 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Molecular Modeling and Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Açaí Constituents against NLRP3 Inflammasome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8112. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158112. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125681 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Structure and Inhibition of a Malaria Drug Target: Geranylgeranyl Diphosphate Synthase.Biochemistry. 2016 Sep 13;55(36):5180-90. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00398. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27564465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perutz M. Electrostatic effects in proteins. Science. 1978;201:1187–1191. - PubMed
-
- Honig B., Nicholls A. Classical electrostatics in biology and chemistry. Science. 1995;268:1144. - PubMed
-
- Davis M.E., McCammon J.A. Electrostatics in biomolecular structure and dynamics. Chem. Rev. 1990;94:7684–7692.
-
- Baker N.A., McCammon J.A. Electrostatic Interactions. In: Bourne P., Weissig H., editors. Structural Bioinformatics. NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2002. pp. 427–440.
-
- Warshel A., Åqvist J. Electrostatic energy and macromolecular function. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1991;20:267–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

