Allosteric modulation of the adenosine family of receptors
- PMID: 15974932
- PMCID: PMC3431557
- DOI: 10.2174/1389557054023242
Allosteric modulation of the adenosine family of receptors
Abstract
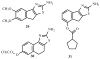
Allosteric modulators for adenosine receptors (ARs) are of an increasing interest and may have potential therapeutic advantage over orthosteric ligands. Benzoylthiophene derivatives (including PD 81,723), 2-aminothiazolium salts, and related allosteric modulators of the A(1) AR have been studied. The benzoylthiophene derivatives were demonstrated to be selective enhancers for the A(1) AR, with little or no effect on other subtypes of ARs. Allosteric modulation of the A(2A) AR has also been reported. A(3) allosteric enhancers may be predicted to be useful against ischemic conditions. We have recently characterized two classes of A(3) AR allosteric modulators: 3-(2-pyridinyl)isoquinolines (e.g. VUF5455) and 1H-imidazo-[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines (e.g. DU124183), which selectively decreased the agonist dissociation rate at the human A(3)AR but not at A(1) and A(2A) ARs. DU124183 left-shifted the agonist conc.-response curve for inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation in intact cells expressing the human A(3)AR with up to 30% potentiation of the maximal efficacy. The increased potency of A(3) agonists was evident only in the presence of an A(3) antagonist, since VUF5455 and DU124183 also antagonized, i.e. displaced binding at the orthosteric site, with K(i) values of 1.68 and 0.82 microM, respectively. A(3)AR mutagenesis studies implicated F182(5.43) and N274(7.45) in the action of the enhancers and was interpreted using a rhodopsin-based A(3)AR molecular model, suggesting multiple binding modes. Amiloride analogues, SCH-202676 (N-(2,3-diphenyl-1,2,4-thiadiazol-5(2H)-ylidene)methanamine), and sodium ions were demonstrated to be common allosteric modulators for at least three subtypes (A(1), A(2A), and A(3)) of ARs.
Figures
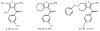
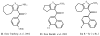

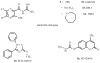
Similar articles
-
Identification of essential residues involved in the allosteric modulation of the human A(3) adenosine receptor.Mol Pharmacol. 2003 May;63(5):1021-31. doi: 10.1124/mol.63.5.1021. Mol Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12695530 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8(8):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32851663 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7(7):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4 PMID: 28752910 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Introduction to adenosine receptors as therapeutic targets.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(193):1-24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-89615-9_1. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19639277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric modulation of adenosine receptors.Purinergic Signal. 2009 Mar;5(1):51-61. doi: 10.1007/s11302-008-9105-3. Epub 2008 Jul 10. Purinergic Signal. 2009. PMID: 18615273 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulation of purine and pyrimidine receptors.Adv Pharmacol. 2011;61:187-220. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385526-8.00007-2. Adv Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21586360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Invited Lectures : Overviews Purinergic signalling: past, present and future.Purinergic Signal. 2006 May;2(1):1-324. doi: 10.1007/s11302-006-9006-2. Epub 2006 May 15. Purinergic Signal. 2006. PMID: 18404494 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Molecular mechanism of allosteric modulation at GPCRs: insight from a binding kinetics study at the human A1 adenosine receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;171(23):5295-312. doi: 10.1111/bph.12836. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25040887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christopoulos A. Nature Rev Drug Disc. 2002;1:198–210. - PubMed
-
- Christopoulos A, Kenakin T. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:323–374. - PubMed
-
- Olin J, Schneider L. Cochrane Database System Review. 2002:CD001747. - PubMed
-
- Jarvis MF, Gessner G, Shapiro G, Merkel L, Myers M, Cox BF, Martin GE. Brain Res. 1999;840:75–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

