Role of IL-17A, IL-17F, and the IL-17 receptor in regulating growth-related oncogene-alpha and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in bronchial epithelium: implications for airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 15972674
- PMCID: PMC2849297
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.404
Role of IL-17A, IL-17F, and the IL-17 receptor in regulating growth-related oncogene-alpha and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in bronchial epithelium: implications for airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis
Abstract
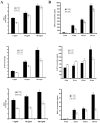
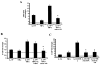
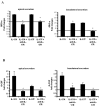
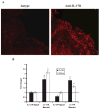
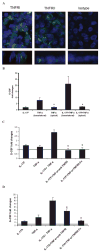
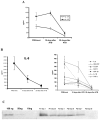
IL-17R signaling is critical for pulmonary neutrophil recruitment and host defense against Gram-negative bacteria through the coordinated release of G-CSF and CXC chemokine elaboration. In this study, we show that IL-17R is localized to basal airway cells in human lung tissue, and functional IL-17R signaling occurs on the basolateral surface of human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells. IL-17A and IL-17F were potent inducers of growth-related oncogene-alpha and G-CSF in HBE cells, and significant synergism was observed with TNF-alpha largely due to signaling via TNFRI. The activities of both IL-17A and IL-17F were blocked by a specific anti-IL-17R Ab, but only IL-17A was blocked with a soluble IL-17R, suggesting that cell membrane IL-17R is required for signaling by both IL-17A and IL-17F. Because IL-17A and IL-17F both regulate lung neutrophil recruitment, we measured these molecules as well as the proximal regulator IL-23p19 in the sputum of patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) undergoing pulmonary exacerbation. We found significantly elevated levels of these molecules in the sputum of patients with CF who were colonized with Pseudomonas aeruginosa at the time of pulmonary exacerbation, and the levels declined with therapy directed against P. aeruginosa. IL-23 and the downstream cytokines IL-17A and IL-17F are critical molecules for proinflammatory gene expression in HBE cells and are likely involved in the proinflammatory cytokine network involved with CF pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Requirement of interleukin 17 receptor signaling for lung CXC chemokine and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor expression, neutrophil recruitment, and host defense.J Exp Med. 2001 Aug 20;194(4):519-27. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.4.519. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11514607 Free PMC article.
-
A distinct regulatory role of Th17 cytokines IL-17A and IL-17F in chemokine secretion from lung microvascular endothelial cells.Inflammation. 2012 Jun;35(3):1119-31. doi: 10.1007/s10753-011-9419-0. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 22219048
-
IL-17A and IL-17F stimulate chemokines via MAPK pathways (ERK1/2 and p38 but not JNK) in mouse cultured mesangial cells: synergy with TNF-alpha and IL-1beta.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):F779-87. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00198.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20042461
-
Interleukin-17 in pulmonary host defense.Exp Lung Res. 2007 Dec;33(10):507-18. doi: 10.1080/01902140701756604. Exp Lung Res. 2007. PMID: 18075825 Review.
-
Signaling of interleukin-17 family cytokines in immunity and inflammation.Cell Signal. 2011 Jul;23(7):1069-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.11.022. Epub 2010 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21130872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Th17-stimulating protein vaccines confer protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Sep 1;186(5):420-7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201202-0182OC. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22723292 Free PMC article.
-
CFTR, mucins, and mucus obstruction in cystic fibrosis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 Sep 1;2(9):a009589. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009589. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 22951447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cell unresponsiveness in a pediatric cystic fibrosis patient: a case report.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2014 Jan 17;10(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-10-2. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24438707 Free PMC article.
-
The T helper type 17/regulatory T cell imbalance was associated with Ras-GTPase overexpression in patients with pulmonary hypertension associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Immunology. 2019 Aug;157(4):304-311. doi: 10.1111/imm.13084. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Immunology. 2019. PMID: 31141166 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
IL-17 family: cytokines, receptors and signaling.Cytokine. 2013 Nov;64(2):477-85. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.07.022. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Cytokine. 2013. PMID: 24011563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yao Z, Painter SL, Fanslow WC, Ulrich D, Macduff BM, Spriggs MK, Armitage RJ. Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J Immunol. 1995;155:5483–5486. - PubMed
-
- Ye P, Rodriguez FH, Kanaly S, Stocking KL, Schurr J, Schwarzenberger P, Oliver P, Huang W, Zhang P, Zhang J, et al. Requirement of interleukin 17 receptor signaling for lung CXC chemokine and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor expression, neutrophil recruitment, and host defense. J Exp Med. 2001;194:519–528. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kolls JK, Kanaly ST, Ramsay AJ. Interleukin-17: an emerging role in lung inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;28:9–11. - PubMed
-
- Laan M, Cui ZH, Hoshino H, Lötvall J, Sjöstrand M, Gruenert DC, Skoogh BE, Lindén A. Neutrophil recruitment by human IL-17 via C-X-C chemokine release in the airways. J Immunol. 1999;162:2347–2352. - PubMed
-
- Lindén A, Hoshino H, Laan M. Airway neutrophils and interleukin-17. Eur Respir J. 2000;15:973–977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

