Simultaneous recruitment of coactivators by Gcn4p stimulates multiple steps of transcription in vivo
- PMID: 15964818
- PMCID: PMC1156971
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5626-5638.2005
Simultaneous recruitment of coactivators by Gcn4p stimulates multiple steps of transcription in vivo
Abstract
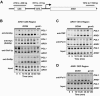
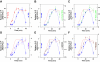
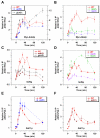
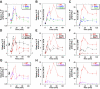
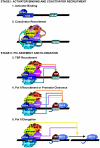
Transcriptional activation by Gcn4p is dependent on the coactivators SWI/SNF, SAGA, and Srb Mediator, which are recruited by Gcn4p and stimulate assembly of the pre-initiation complex (PIC) at the ARG1 promoter in vivo. We show that recruitment of all three coactivators is nearly simultaneous with binding of Gcn4p at ARG1 and is followed quickly by PIC formation and elongation by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) through the open reading frame. Despite the simultaneous recruitment of coactivators, rapid recruitment of SWI/SNF depends on the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) subunit of SAGA (Gcn5p), a non-HAT function of SAGA, and on Mediator. SAGA recruitment in turn is strongly stimulated by Mediator and the RSC complex. Recruitment of Mediator, by contrast, occurs independently of the other coactivators at ARG1. We confirm the roles of Mediator and SAGA in TATA binding protein (TBP) recruitment and demonstrate that all four coactivators under study enhance Pol II recruitment or promoter clearance following TBP binding. We also present evidence that SWI/SNF and SAGA stimulate transcription elongation downstream from the promoter. These functions can be limited to discrete time intervals, providing evidence for multiple stages in the induction process. Our findings reveal a program of coactivator recruitment and PIC assembly that distinguishes Gcn4p from other yeast activators studied thus far.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interdependent recruitment of SAGA and Srb mediator by transcriptional activator Gcn4p.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 May;25(9):3461-74. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.9.3461-3474.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15831453 Free PMC article.
-
An array of coactivators is required for optimal recruitment of TATA binding protein and RNA polymerase II by promoter-bound Gcn4p.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 May;24(10):4104-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.10.4104-4117.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15121833 Free PMC article.
-
SAGA is an essential in vivo target of the yeast acidic activator Gal4p.Genes Dev. 2001 Aug 1;15(15):1935-45. doi: 10.1101/gad.911401. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11485988 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of chromatin remodelling factors during gene activation via the glucocorticoid receptor N-terminal domain.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):410-4. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961930 Review.
-
TAFs mediate transcriptional activation and promoter selectivity.Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Sep;21(9):338-42. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996. PMID: 8870497 Review.
Cited by
-
Fungal mediator tail subunits contain classical transcriptional activation domains.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;35(8):1363-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01508-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25645928 Free PMC article.
-
Vps factors are required for efficient transcription elongation in budding yeast.Genetics. 2013 Mar;193(3):829-51. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.146308. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23335340 Free PMC article.
-
TFIID and Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase functions probed by genome-wide synthetic genetic array analysis using a Saccharomyces cerevisiae taf9-ts allele.Genetics. 2005 Nov;171(3):959-73. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.046557. Epub 2005 Aug 22. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 16118188 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of a poised RNAPII-dependent promoter requires both SAGA and mediator.Genetics. 2010 Mar;184(3):659-72. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.113464. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Genetics. 2010. PMID: 20048049 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct regulatory mechanisms of eukaryotic transcriptional activation by SAGA and TFIID.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Feb;1809(2):97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.08.009. Epub 2010 Aug 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20800707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
